Page 135 - Introduction to Paleobiology and The Fossil Record
P. 135
122 INTRODUCTION TO PALEOBIOLOGY AND THE FOSSIL RECORD
geographic barrier
species B species C
species A species B
Time
isolation
environmental crisis
or random event
species A
species A
(a) (b)
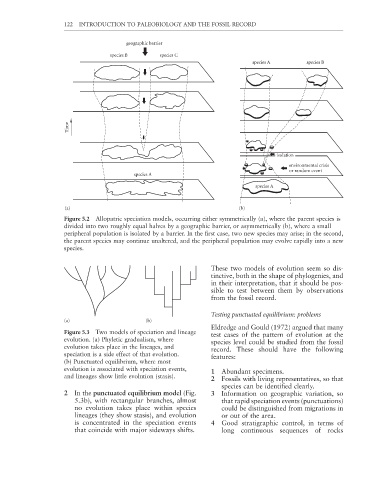
Figure 5.2 Allopatric speciation models, occurring either symmetrically (a), where the parent species is
divided into two roughly equal halves by a geographic barrier, or asymmetrically (b), where a small
peripheral population is isolated by a barrier. In the first case, two new species may arise; in the second,
the parent species may continue unaltered, and the peripheral population may evolve rapidly into a new
species.
These two models of evolution seem so dis-
tinctive, both in the shape of phylogenies, and
in their interpretation, that it should be pos-
sible to test between them by observations
from the fossil record.
Testing punctuated equilibrium: problems
(a) (b)
Eldredge and Gould (1972) argued that many
Figure 5.3 Two models of speciation and lineage test cases of the pattern of evolution at the
evolution. (a) Phyletic gradualism, where species level could be studied from the fossil
evolution takes place in the lineages, and record. These should have the following
speciation is a side effect of that evolution. features:
(b) Punctuated equilibrium, where most
evolution is associated with speciation events, 1 Abundant specimens.
and lineages show little evolution (stasis).
2 Fossils with living representatives, so that
species can be identifi ed clearly.
2 In the punctuated equilibrium model (Fig. 3 Information on geographic variation, so
5.3b), with rectangular branches, almost that rapid speciation events (punctuations)
no evolution takes place within species could be distinguished from migrations in
lineages (they show stasis), and evolution or out of the area.
is concentrated in the speciation events 4 Good stratigraphic control, in terms of
that coincide with major sideways shifts. long continuous sequences of rocks