Page 329 - Introduction to Paleobiology and The Fossil Record
P. 329
316 INTRODUCTION TO PALEOBIOLOGY AND THE FOSSIL RECORD
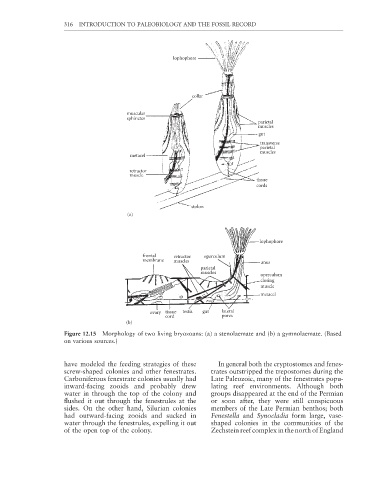
lophophore
collar
muscular
sphincter
parietal
muscles
gut
transverse
parietal
muscles
metacel
retractor
muscle
tissue
cords
stolon
(a)
lophophore
frontal retractor operculum
membrane muscles anus
parietal
muscles
operculum
closing
muscle
metacel
ovary tissue testis gut lateral
cord pores
(b)
Figure 12.15 Morphology of two living bryozoans: (a) a stenolaemate and (b) a gymnolaemate. (Based
on various sources.)
have modeled the feeding strategies of these In general both the cryptostomes and fenes-
screw-shaped colonies and other fenestrates. trates outstripped the trepostomes during the
Carboniferous fenestrate colonies usually had Late Paleozoic, many of the fenestrates popu-
inward-facing zooids and probably drew lating reef environments. Although both
water in through the top of the colony and groups disappeared at the end of the Permian
flushed it out through the fenestrules at the or soon after, they were still conspicuous
sides. On the other hand, Silurian colonies members of the Late Permian benthos; both
had outward-facing zooids and sucked in Fenestella and Synocladia form large, vase-
water through the fenestrules, expelling it out shaped colonies in the communities of the
of the open top of the colony. Zechstein reef complex in the north of England