Page 88 - Introduction to Petroleum Engineering
P. 88
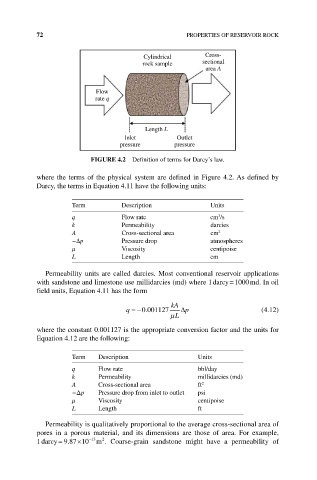
72 PROPERTIES OF RESERVOIR ROCK
Cylindrical Cross-
rock sample sectional
area A
Flow
rate q
Length L
Inlet Outlet
pressure pressure
FIguRE 4.2 Definition of terms for Darcy’s law.
where the terms of the physical system are defined in Figure 4.2. As defined by
Darcy, the terms in Equation 4.11 have the following units:
Term Description Units
3
q Flow rate cm /s
k Permeability darcies
A Cross‐sectional area cm 2
−∆p Pressure drop atmospheres
μ Viscosity centipoise
L Length cm
Permeability units are called darcies. Most conventional reservoir applications
with sandstone and limestone use millidarcies (md) where 1 darcy = 1000 md. In oil
field units, Equation 4.11 has the form
kA
.
q =−0 001127 ∆ p (4.12)
µ L
where the constant 0.001127 is the appropriate conversion factor and the units for
Equation 4.12 are the following:
Term Description Units
q Flow rate bbl/day
k Permeability millidarcies (md)
A Cross‐sectional area ft 2
−Δp Pressure drop from inlet to outlet psi
μ Viscosity centipoise
L Length ft
Permeability is qualitatively proportional to the average cross‐sectional area of
pores in a porous material, and its dimensions are those of area. For example,
2
1 darcy = 98710. × −13 m . Coarse‐grain sandstone might have a permeability of