Page 167 - Introduction to Transfer Phenomena in PEM Fuel Cells
P. 167
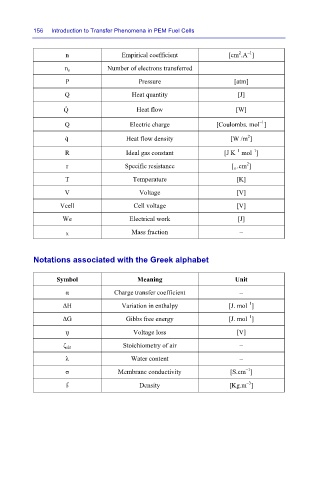
156 Introduction to Transfer Phenomena in PEM Fuel Cells
–1
2
n
Empirical coefficient
–
n e
Pressure
P Number of electrons transferred [cm .A ]
[atm]
Q Heat quantity [J]
Q Heat flow [W]
–1
Q Electric charge [Coulombs. mol ]
q Heat flow density [W /m ]
2
–1
–1
R Ideal gas constant [J K mol ]
2
r Specific resistance [ Ω .cm ]
T Temperature [K]
V Voltage [V]
Vcell Cell voltage [V]
We Electrical work [J]
X Mass fraction –
Notations associated with the Greek alphabet
Symbol Meaning Unit
α Charge transfer coefficient –
–1
ΔH Variation in enthalpy [J. mol ]
–1
ΔG Gibbs free energy [J. mol ]
ߟ Voltage loss [V]
ζ air Stoichiometry of air –
λ Water content –
–1
σ Membrane conductivity [S.cm ]
ρ Density [Kg.m ]
–3