Page 107 - Introduction to chemical reaction engineering and kinetics
P. 107
5.1 Types and Examples of Complex Systems 89
(This network is series with respect to the chlorinated species and parallel with
respect to Cl,.)
l Hepatic metabolism of lidocaine (LID, C,,H,,N,O) W
This follows a series-parallel network, corresponding to either hydroxylation of
the benzene ring, or de-ethylation of the tertiary amine, leading to MEGX, to
hydroxylidocaine, and ultimately to hydroxyMEGX:
LID -c2Hs MEGX (C,,H,,N20)
LID 2 hydroxylidocaine ( Ci4HZ2N202)
MEGX +OH hydroxyMEGX (C,,H,sN,O,)
hydroxylidocaine --+ hydroxyMEGX
-CzHs
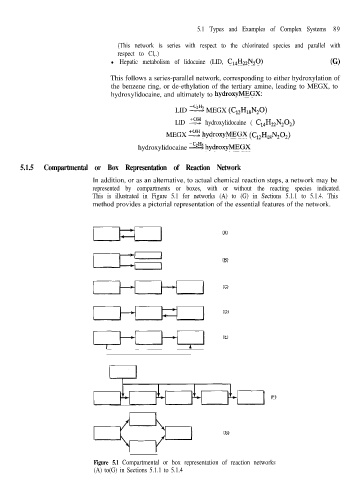
5.1.5 Compartmental or Box Representation of Reaction Network
In addition, or as an alternative, to actual chemical reaction steps, a network may be
represented by compartments or boxes, with or without the reacting species indicated.
This is illustrated in Figure 5.1 for networks (A) to (G) in Sections 5.1.1 to 5.1.4. This
method provides a pictorial representation of the essential features of the network.
(A)
(B)
CC)
(D)
(E)
(F)
(G)
Figure 5.1 Compartmental or box representation of reaction networks
(A) to(G) in Sections 5.1.1 to 5.1.4