Page 54 -
P. 54
The Knowledge Management Cycle 37
Sources Repository Reports Users
of research
newsletters
bulletins
results
Acquire Refine Store Distribute Present
Calls and Analyze,
surveys interpret, report
Edit and format
Decompose into Indexed and Online via Web Interactive
k units, index, linked and groupware selection of
and link knowledge units knowledge units
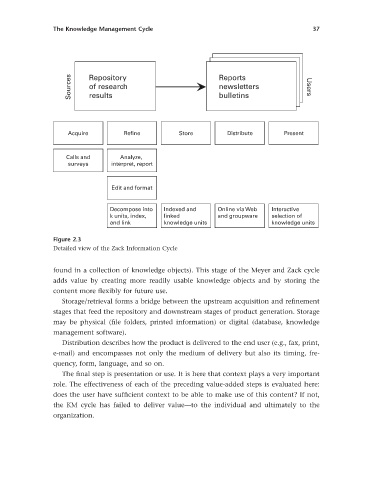
Figure 2.3
Detailed view of the Zack Information Cycle
found in a collection of knowledge objects). This stage of the Meyer and Zack cycle
adds value by creating more readily usable knowledge objects and by storing the
content more fl exibly for future use.
Storage/retrieval forms a bridge between the upstream acquisition and refi nement
stages that feed the repository and downstream stages of product generation. Storage
may be physical (fi le folders, printed information) or digital (database, knowledge
management software).
Distribution describes how the product is delivered to the end user (e.g., fax, print,
e-mail) and encompasses not only the medium of delivery but also its timing, fre-
quency, form, language, and so on.
The fi nal step is presentation or use. It is here that context plays a very important
role. The effectiveness of each of the preceding value-added steps is evaluated here:
does the user have suffi cient context to be able to make use of this content? If not,
the KM cycle has failed to deliver value — to the individual and ultimately to the
organization.