Page 122 -
P. 122
243_MasterPieces_02b.qxd 4/18/03 6:59 PM Page 94
94 Masterpiece 2 • The Learning Brick Sorter
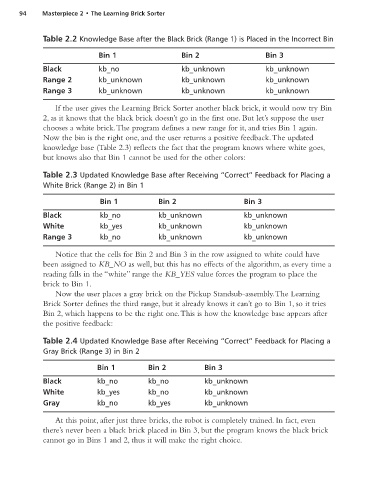
Table 2.2 Knowledge Base after the Black Brick (Range 1) is Placed in the Incorrect Bin
Bin 1 Bin 2 Bin 3
Black kb_no kb_unknown kb_unknown
Range 2 kb_unknown kb_unknown kb_unknown
Range 3 kb_unknown kb_unknown kb_unknown
If the user gives the Learning Brick Sorter another black brick, it would now try Bin
2, as it knows that the black brick doesn’t go in the first one. But let’s suppose the user
chooses a white brick.The program defines a new range for it, and tries Bin 1 again.
Now the bin is the right one, and the user returns a positive feedback.The updated
knowledge base (Table 2.3) reflects the fact that the program knows where white goes,
but knows also that Bin 1 cannot be used for the other colors:
Table 2.3 Updated Knowledge Base after Receiving “Correct” Feedback for Placing a
White Brick (Range 2) in Bin 1
Bin 1 Bin 2 Bin 3
Black kb_no kb_unknown kb_unknown
White kb_yes kb_unknown kb_unknown
Range 3 kb_no kb_unknown kb_unknown
Notice that the cells for Bin 2 and Bin 3 in the row assigned to white could have
been assigned to KB_NO as well, but this has no effects of the algorithm, as every time a
reading falls in the “white” range the KB_YES value forces the program to place the
brick to Bin 1.
Now the user places a gray brick on the Pickup Standsub-assembly.The Learning
Brick Sorter defines the third range, but it already knows it can’t go to Bin 1, so it tries
Bin 2, which happens to be the right one.This is how the knowledge base appears after
the positive feedback:
Table 2.4 Updated Knowledge Base after Receiving “Correct” Feedback for Placing a
Gray Brick (Range 3) in Bin 2
Bin 1 Bin 2 Bin 3
Black kb_no kb_no kb_unknown
White kb_yes kb_no kb_unknown
Gray kb_no kb_yes kb_unknown
At this point, after just three bricks, the robot is completely trained. In fact, even
there’s never been a black brick placed in Bin 3, but the program knows the black brick
cannot go in Bins 1 and 2, thus it will make the right choice.