Page 107 - Laboratory Manual in Physical Geology
P. 107
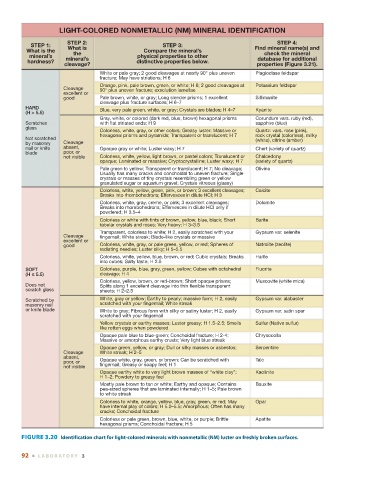
LIGHT-COLORED NONMETALLIC (NM) MINERAL IDENTIFICATION
STEP 2: STEP 4:
STEP 1: What is STEP 3: Find mineral name(s) and
What is the the Compare the mineral’s check the mineral
mineral’s mineral’s physical properties to other database for additional
hardness? distinctive properties below.
cleavage? properties (Figure 3.21).
White or pale gray; 2 good cleavages at nearly 90° plus uneven Plagioclase feldspar
fracture; May have striations; H 6
Orange, pink, pale brown, green, or white; H 6; 2 good cleavages at Potassium feldspar
Cleavage 90° plus uneven fracture; exsolution lamellae
excellent or
good Pale brown, white, or gray; Long slender prisms; 1 excellent Sillimanite
cleavage plus fracture surfaces; H 6–7
HARD Blue, very pale green, white, or gray; Crystals are blades; H 4–7 Kyanite
(H > 5.5)
Gray, white, or colored (dark red, blue, brown) hexagonal prisms Corundum vars. ruby (red),
Scratches with flat striated ends; H 9 sapphire (blue)
glass
Colorless, white, gray, or other colors; Greasy luster; Massive or Quartz: vars. rose (pink),
hexagonal prisms and pyramids; Transparent or translucent; H 7 rock crystal (colorless), milky
Not scratched (white), citrine (amber)
by masonry Cleavage
nail or knife absent, Opaque gray or white; Luster waxy; H 7 Chert (variety of quartz)
blade poor, or
not visible Colorless, white, yellow, light brown, or pastel colors; Translucent or Chalcedony
opaque; Laminated or massive; Cryptocrystalline; Luster waxy; H 7 (variety of quartz)
Pale green to yellow; Transparent or translucent; H 7; No cleavage; Olivine
Usually has many cracks and conchoidal to uneven fracture; Single
crystals or masses of tiny crystals resembling green or yellow
granulated sugar or aquarium gravel; Crystals vitreous (glassy)
Colorless, white, yellow, green, pink, or brown; 3 excellent cleavages; Calcite
Breaks into rhombohedrons; Effervesces in dilute HCI; H 3
Colorless, white, gray, creme, or pink; 3 excellent cleavages; Dolomite
Breaks into rhombohedrons; Effervesces in dilute HCI only if
powdered; H 3.5–4
Colorless or white with tints of brown, yellow, blue, black; Short Barite
tabular crystals and roses; Very heavy; H 3–3.5
Transparent, colorless to white; H 2, easily scratched with your Gypsum var. selenite
Cleavage fingernail; White streak; Blade-like crystals or massive
excellent or
good Colorless, white, gray, or pale green, yellow, or red; Spheres of Natrolite (zeolite)
radiating needles; Luster silky; H 5–5.5
Colorless, white, yellow, blue, brown, or red; Cubic crystals; Breaks Halite
into cubes; Salty taste; H 2.5
SOFT Colorless, purple, blue, gray, green, yellow; Cubes with octahedral Fluorite
(H < 5.5) cleavage; H 4
Colorless, yellow, brown, or red-brown; Short opaque prisms; Muscovite (white mica)
Does not Splits along 1 excellent cleavage into thin flexible transparent
scratch glass sheets; H 2–2.5
Scratched by White, gray or yellow; Earthy to pearly; massive form; H 2, easily Gypsum var. alabaster
masonry nail scratched with your fingernail; White streak
or knife blade White to gray; Fibrous form with silky or satiny luster; H 2, easily Gypsum var. satin spar
scratched with your fingernail
Yellow crystals or earthy masses; Luster greasy; H 1.5–2.5; Smells Sulfur (Native sulfur)
like rotten eggs when powdered
Opaque pale blue to blue-green; Conchoidal fracture; H 2-4; Chrysocolla
Massive or amorphous earthy crusts; Very light blue streak
Opaque green, yellow, or gray; Dull or silky masses or asbestos; Serpentine
Cleavage White streak; H 2–5
absent, Opaque white, gray, green, or brown; Can be scratched with Talc
poor, or fingernail; Greasy or soapy feel; H 1
not visible
Opaque earthy white to very light brown masses of “white clay”; Kaolinite
H 1–2; Powdery to greasy feel
Mostly pale brown to tan or white; Earthy and opaque; Contains Bauxite
pea-sized spheres that are laminated internally; H 1–5; Pale brown
to white streak
Colorless to white, orange, yellow, blue, gray, green, or red; May Opal
have internal play of colors; H 5.0–5.5; Amorphous; Often has many
cracks; Conchoidal fracture
Colorless or pale green, brown, blue, white, or purple; Brittle Apatite
hexagonal prisms; Conchoidal fracture; H 5
FIGURE 3.20 Identification chart for light-colored minerals with nonmetallic (NM) luster on freshly broken surfaces.
92 ■ L ABOR ATORY 3