Page 118 - Laboratory Manual in Physical Geology
P. 118
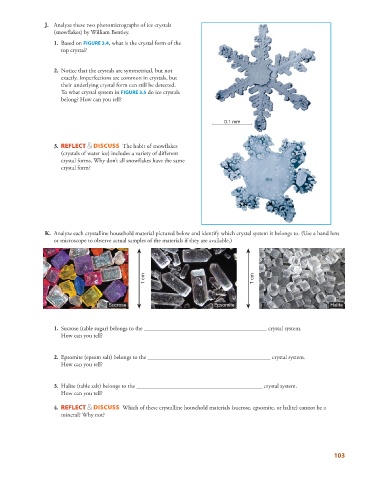
J. Analyze these two photomicrographs of ice crystals
(snowflakes) by William Bentley.
1. Based on FIGURE 3.4 , what is the crystal form of the
top crystal?
2. Notice that the crystals are symmetrical, but not
exactly. Imperfections are common in crystals, but
their underlying crystal form can still be detected.
To what crystal system in FIGURE 3.5 do ice crystals
belong? How can you tell?
0.1 mm
3. REFLECT & DISCUSS The habit of snowflakes
(crystals of water ice) includes a variety of different
crystal forms. Why don’t all snowflakes have the same
crystal form?
K. Analyze each crystalline household material pictured below and identify which crystal system it belongs to. (Use a hand lens
or microscope to observe actual samples of the materials if they are available.)
1 cm 1 cm
Sucrose Epsomite Halite
1. Sucrose (table sugar) belongs to the _________________________________________ crystal system.
How can you tell?
2. Epsomite (epsom salt) belongs to the _________________________________________ crystal system.
How can you tell?
3. Halite (table salt) belongs to the __________________________________________ crystal system.
How can you tell?
4. REFLECT & DISCUSS Which of these crystalline household materials (sucrose, epsomite, or halite) cannot be a
mineral? Why not?
103