Page 151 - Laboratory Manual in Physical Geology
P. 151
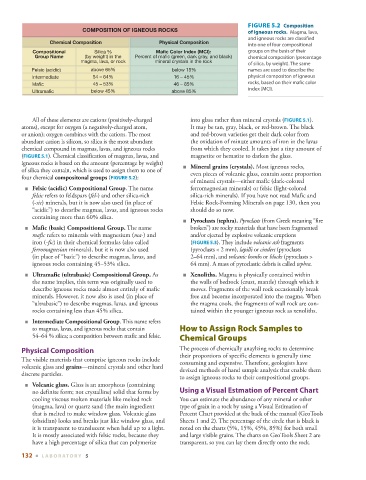
FIGURE 5.2 Composition
COMPOSITION OF IGNEOUS ROCKS of igneous rocks. Magma, lava,
and igneous rocks are classified
Chemical Composition Physical Composition
into one of four compositional
Compositional Silica % Mafic Color Index (MCI): groups on the basis of their
Group Name (by weight) in the Percent of mafic (green, dark gray, and black) chemical composition (percentage
magma, lava, or rock mineral crystals in the rock
of silica, by weight). The same
Felsic (acidic) above 65% below 15% names are used to describe the
Intermediate 54 – 64% 16 – 45% physical compositon of igneous
Mafic 45 – 53% 46 – 85% rocks, based on their mafic color
index (MCI).
Ultramafic below 45% above 85%
All of these elements are cations (positively-charged into glass rather than mineral crystals ( FIGURE 5.1 ).
atoms), except for oxygen (a negatively-charged atom, It may be tan, gray, black, or red-brown. The black
or anion); oxygen combines with the cations. The most and red-brown varieties get their dark color from
abundant cation is silicon, so silica is the most abundant the oxidation of minute amounts of iron in the lavas
chemical compound in magmas, lavas, and igneous rocks from which they cooled. It takes just a tiny amount of
( FIGURE 5.1 ). Chemical classification of magmas, lavas, and magnetite or hematite to darken the glass.
igneous rocks is based on the amount (percentage by weight) ■ Mineral grains (crystals) . Most igneous rocks,
of silica they contain, which is used to assign them to one of even pieces of volcanic glass, contain some proportion
four chemical compositonal groups ( FIGURE 5.2 ):
of mineral crystals—either mafic (dark-colored
■ Felsic (acidic) Compositional Group . The name ferromagnesian minerals) or felsic (light-colored
felsic refers to feldspars ( fel -) and other silica-rich silica-rich minerals). If you have not read Mafic and
(- sic ) minerals, but it is now also used (in place of Felsic Rock-Forming Minerals on page 130 , then you
“acidic”) to decsribe magmas, lavas, and igneous rocks should do so now.
containing more than 60% silica.
■ Pyroclasts (tephra) . Pyroclasts (from Greek meaning “fire
■ Mafic (basic) Compositional Group . The name broken”) are rocky materials that have been fragmented
mafic refers to minerals with magnesium ( ma -) and and/or ejected by explosive volcanic eruptions
iron (- fic ) in their chemical formulas (also called ( FIGURE 5.3 ). They include volcanic ash fragments
ferromagnesian minerals), but it is now also used (pyroclasts < 2 mm), lapilli or cinders (pyroclasts
(in place of “basic”) to describe magmas, lavas, and 2–64 mm), and volcanic bombs or blocks (pyroclasts >
igneous rocks containing 45–53% silica. 64 mm). A mass of pyroclastic debris is called tephra .
■ Ultramafic (ultrabasic) Compositional Group . As ■ Xenoliths . Magma is physically contained within
the name implies, this term was originally used to the walls of bedrock (crust, mantle) through which it
describe igneous rocks made almost entirely of mafic moves. Fragments of the wall rock occasionally break
minerals. However, it now also is used (in place of free and become incorporated into the magma. When
“ultrabasic”) to describe magmas, lavas, and igneous the magma cools, the fragments of wall rock are con-
rocks containing less than 45% silica. tained within the younger igneous rock as xenoliths.
■ Intermediate Compositional Group . This name refers
to magmas, lavas, and igneous rocks that contain How to Assign Rock Samples to
54–64 % silica; a composition between mafic and felsic. Chemical Groups
Physical Composition The process of chemically anaylzing rocks to determine
their proportions of specific elements is generally time
The visible materials that comprise igneous rocks include consuming and expensive. Therefore, geologists have
volcanic glass and grains —mineral crystals and other hard devised methods of hand sample analysis that enable them
discrete particles.
to assign igneous rocks to their compositional groups.
■ Volcanic glass . Glass is an amorphous (containing
no definite form; not crystalline) solid that forms by Using a Visual Estmation of Percent Chart
cooling viscous molten materials like melted rock You can estimate the abundance of any mineral or other
(magma, lava) or quartz sand (the main ingredient type of grain in a rock by using a Visual Estimation of
that is melted to make window glass. Volcanic glass Percent Chart provided at the back of the manual (GeoTools
(obsidian) looks and breaks just like window glass, and Sheets 1 and 2). The percentage of the circle that is black is
it is transparent to translucent when held up to a light. noted on the charts (5%, 15%, 45%, 85%) for both small
It is mostly associated with felsic rocks, because they and large visible grains. The charts on GeoTools Sheet 2 are
have a high percentage of silica that can polymerize transparent, so you can lay them directly onto the rock.
132 ■ L ABOR ATORY 5