Page 215 - Laboratory Manual in Physical Geology
P. 215
aragonite seashells or calcite mineral crystals will both Directed stress occurs on a large scale at convergent plate
recrystallize to a mass of small equal-sized crystals in boundaries, where the edges of two plates push together.
the metamorphic rock called marble. Quartz sandstone
becomes quartzite.
Temperature Effects on Rocks
Directed pressure (differential stress) is pressure that Temperature is a measure of thermal energy. The greater
is not equal in all directions. This causes the rock to the thermal energy, the higher the temperature and more
get more compressed in one direction than any other energized the atoms and molecules are in the rock. When
( FIGURE 7.3 ). If you roll a lump of dough into a ball, temperature exceeds 200°C (twice the boiling point of water),
then you are rolling and squeezing it equally in all direc- the molecules get highly energized. If the rock is under
tions to make the ball. But if you place the dough on a directed pressure, then it may fold in a ductile (like plastic)
table and press on it with your hand, it gets squashed manner and become foliated. ( FIGURE 7.4 ). Some bonds in the
and shortened in the direction of the directed pressure. minerals begin to break and reform in more stable configura-
This causes flat minerals to get foliated —flatten out tions. This may cause recrystallization or neomorphism.
parallel to one another and perpendicular to the stress.
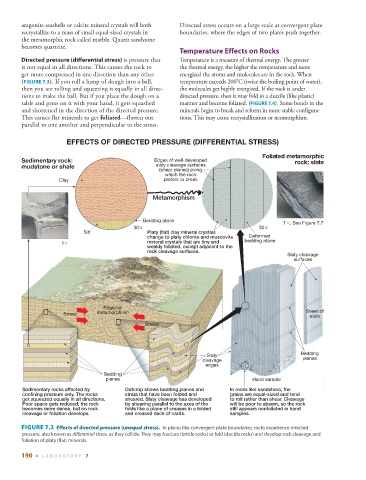
EFFECTS OF DIRECTED PRESSURE (DIFFERENTIAL STRESS)
Foliated metamorphic
Sedimentary rock: Edges of well-developed rock: slate
mudstone or shale slaty cleavage surfaces
(shear planes) along
which the rock
Clay prefers to break
Metamorphism
Bedding plane
1 , See Figure 7.7
30 30
Silt Platy (flat) clay mineral crystals
change to platy chlorite and muscovite Deformed
1 mineral crystals that are tiny and bedding plane
weakly foliated, except adjacent to the
rock cleavage surfaces.
Slaty cleavage
surfaces
Regional
Stress metamorphism Sheet of
slate
Stress
Slaty Bedding
cleavage planes
edges
Bedding
planes Hand sample
Sedimentary rocks affected by Outcrop shows bedding planes and In rocks like sandstone, the
confining pressure only. The rocks strata that have been folded and grains are equal-sized and tend
get squeezed equally in all directions. sheared. Slaty cleavage has developed to roll rather than shear. Cleavage
Poor space gets reduced, the rock by shearing parallel to the axes of the will be poor to absent, so the rock
becomes more dense, but no rock folds like a plane of creases in a folded still appears nonfoliated in hand
cleavage or foliation develops. and creased deck of cards. samples.
FIGURE 7.3 Effects of directed pressure (unequal stress). In places like convergent plate boundaries, rocks experience directed
pressure, also known as differential stress , as they collide. They may fracture (brittle rocks) or fold (ductile rocks) and develop rock cleavage and
foliation of platy (flat) minerals.
190 ■ L ABOR ATORY 7