Page 222 - Laboratory Manual in Physical Geology
P. 222
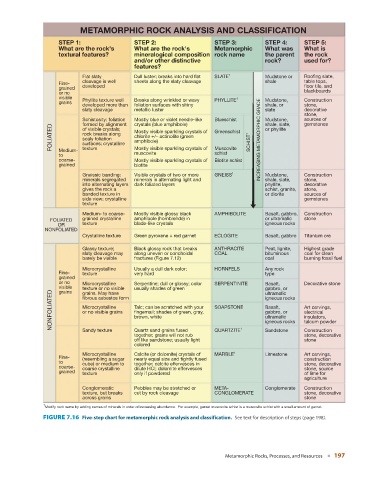
METAMORPHIC ROCK ANALYSIS AND CLASSIFICATION
STEP 1: STEP 2: STEP 3: STEP 4: STEP 5:
What are the rock's What are the rock's Metamorphic What was What is
textural features? mineralogical composition rock name the parent the rock
and/or other distinctive rock? used for?
features?
Flat slaty Dull luster; breaks into hard flat SLATE 1 Mudstone or Roofing slate,
cleavage is well sheets along the slaty cleavage shale table tops,
Fine-
grained developed floor tile, and
or no blackboards
visible Phyllite texture well Breaks along wrinkled or wavy PHYLLITE 1 Mudstone, Construction
grains
developed more than foliation surfaces with shiny shale, or stone,
slaty cleavage metallic luster slate decorative
stone,
Schistosity: foliation Mostly blue or violet needle-like Blueschist Mudstone, sources of
crystals (blue amphibole)
shale, slate,
formed by alignment
gemstones
FOLIATED of visible crystals; Mostly visible sparkling crystals of Greenschist SCHIST 1 INCREASING METAMORPHIC GRADE or phyllite
rock breaks along
chlorite +/– actinolite (green
scaly foliation
amphibole)
surfaces; crystalline
Medium-
muscovite
schist
to texture Mostly visible sparkling crystals of Muscovite
coarse- Mostly visible sparkling crystals of Biotite schist
grained biotite
Gneissic banding: Visible crystals of two or more GNEISS 1 Mudstone, Construction
minerals segregated minerals in alternating light and shale, slate, stone,
into alternating layers dark foliated layers phyllite, decorative
gives the rock a schist, granite, stone,
banded texture in or diorite sources of
side view; crystalline gemstones
texture
Medium- to coarse- Mostly visible glossy black AMPHIBOLITE Basalt, gabbro, Construction
FOLIATED grained crystalline amphibole (hornblende) in or ultramafic stone
OR texture blade-like crystals igneous rocks
NONFOLIATED
Crystalline texture Green pyroxene + red garnet ECLOGITE Basalt, gabbro Titanium ore
Glassy texture; Black glossy rock that breaks ANTHRACITE Peat, lignite, Highest grade
slaty cleavage may along uneven or conchoidal COAL bituminous coal for clean
barely be visible fractures (Figure 7.12) coal burning fossil fuel
Microcrystalline Usually a dull dark color; HORNFELS Any rock
Fine- texture very hard type
grained
or no Microcrystalline Serpentine; dull or glossy; color SERPENTINITE Basalt, Decorative stone
visible texture or no visible usually shades of green gabbro, or
NONFOLIATED Microcrystalline Talc; can be scratched with your SOAPSTONE Basalt, Art carvings,
grains
grains. May have
ultramafic
fibrous asbestos form
igneous rocks
gabbro, or
electrical
or no visible grains
fingernail; shades of green, gray,
ultramafic
brown, white
insulators,
talcum powder
igneous rocks
Quartz sand grains fused
Sandy texture
stone, decorative
together; grains will not rub QUARTZITE 1 Sandstone Construction
off like sandstone; usually light stone
colored
Microcrystalline Calcite (or dolomite) crystals of MARBLE 1 Limestone Art carvings,
Fine- (resembling a sugar nearly equal size and tightly fused construction
to cube) or medium to together; calcite effervesces in stone, decorative
coarse- coarse crystalline dilute HCl; dolomite effervesces stone, source
grained texture only if powdered of lime for
agriculture
Conglomeratic Pebbles may be stretched or META- Conglomerate Construction
texture, but breaks cut by rock cleavage CONGLOMERATE stone, decorative
across grains stone
1
Modify rock name by adding names of minerals in order of increasing abundance. For example, garnet muscovite schist is a muscovite schist with a small amount of garnet.
FIGURE 7.16 Five-step chart for metamorphic rock analysis and classification. See text for description of steps (page 198 ).
Metamorphic Rocks, Processes, and Resources ■ 197