Page 233 - Laboratory Manual in Physical Geology
P. 233
A CTIVIT Y 7.4 Metamorphic Grades and Facies
Name: ______________________________________ Course/Section: ______________________ Date: ___________
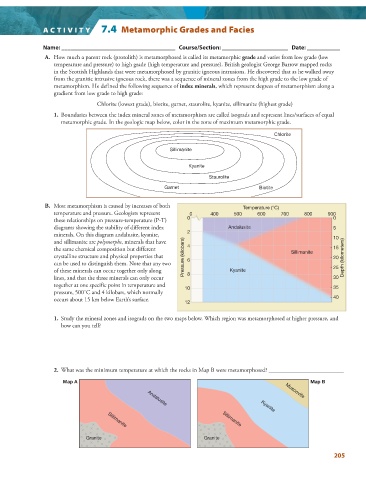
A. How much a parent rock (protolith) is metamorphosed is called its metamorphic grade and varies from low grade (low
temperature and pressure) to high grade (high temperature and pressure). British geologist George Barrow mapped rocks
in the Scottish Highlands that were metamorphosed by granitic igneous intrusions. He discovered that as he walked away
from the granitic intrusive igneous rock, there was a sequence of mineral zones from the high grade to the low grade of
metamorphism. He defined the following sequence of index minerals , which represent degrees of metamorphism along a
gradient from low grade to high grade:
Chlorite (lowest grade), biotite, garnet, staurolite, kyanite, sillimanite (highest grade)
1. Boundaries between the index mineral zones of metamorphism are called isograds and represent lines/surfaces of equal
metamorphic grade. In the geologic map below, color in the zone of maximum metamorphic grade.
Chlorite
Sillimanite
Kyanite
Staurolite
Garnet Biotite
B. Most metamorphism is caused by increases of both Temperature (°C)
temperature and pressure. Geologists represent 0 400 500 600 700 800 900
these relationships on pressure-temperature (P-T) 0 0
diagrams showing the stability of different index Andalusite 5
2
minerals. On this diagram andalusite, kyanite, 10
and sillimanite are polymorphs , minerals that have 4
the same chemical composition but different Sillimanite 15
crystalline structure and physical properties that Pressure (kilobars) 6 20 Depth (kilometers)
can be used to distinguish them. Note that any two 25
of these minerals can occur together only along 8 Kyanite
lines, and that the three minerals can only occur 30
together at one specific point in temperature and
10 35
pressure, 500˚C and 4 kilobars, which normally
occurs about 15 km below Earth’s surface. 40
12
1. Study the mineral zones and isograds on the two maps below. Which region was metamorphosed at higher pressure, and
how can you tell?
2. What was the minimum temperature at which the rocks in Map B were metamorphosed? _________________________
Map A Andalusite Muscovite Map B
+ Sillimanite Sillimanite Kyanite
+ + +
+ + +
+ + + + +
+
+ +
+ + + + + + + +
+ + + + +
Granite + Granite +
+ +
+ + + +
+ + + +
+ + + + + + + + +
205