Page 239 - Laboratory Manual in Physical Geology
P. 239
G F
A
E D
C B
B
C
A
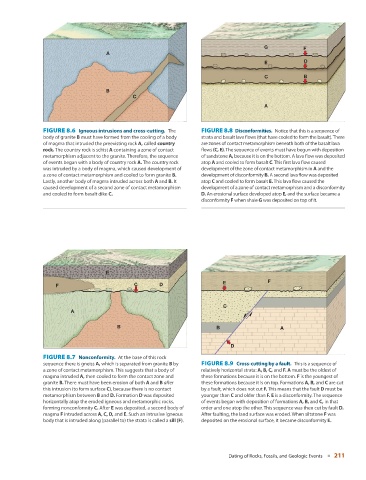
FIGURE 8.6 Igneous intrusions and cross-cutting. The FIGURE 8.8 Disconformities. Notice that this is a sequence of
body of granite B must have formed from the cooling of a body strata and basalt lava flows (that have cooled to form the basalt). There
of magma that intruded the preexisting rock A, called country are zones of contact metamorphism beneath both of the basalt lava
rock. The country rock is schist A containing a zone of contact flows (C, E) . The sequence of events must have begun with deposition
metamorphism adjacent to the granite. Therefore, the sequence of sandstone A , because it is on the bottom. A lava flow was deposited
of events began with a body of country rock A. The country rock atop A and cooled to form basalt C . This first lava flow caused
was intruded by a body of magma, which caused development of development of the zone of contact metamorphism in A and the
a zone of contact metamorphism and cooled to form granite B. development of disconformity B. A second lava flow was deposited
Lastly, another body of magma intruded across both A and B. It atop C and cooled to form basalt E. This lava flow caused the
caused development of a second zone of contact metamorphism development of a zone of contact metamorphism and a disconformity
and cooled to form basalt dike C. D. An erosional surface developed atop E, and the surface became a
disconformity F when shale G was deposited on top of it.
E
F C D E F
C
A
B B A
D
FIGURE 8.7 Nonconformity. At the base of this rock
sequence there is gneiss A, which is separated from granite B by FIGURE 8.9 Cross-cutting by a fault. This is a sequence of
a zone of contact metamorphism. This suggests that a body of relatively horizontal strata: A, B, C, and F. A must be the oldest of
magma intruded A, then cooled to form the contact zone and these formations because it is on the bottom. F is the youngest of
granite B. There must have been erosion of both A and B after these formations because it is on top. Formations A, B, and C are cut
this intrusion (to form surface C ), because there is no contact by a fault, which does not cut F. This means that the fault D must be
metamorphism between B and D. Formation D was deposited younger than C and older than F. E is a disconformity. The sequence
horizontally atop the eroded igneous and metamorphic rocks, of events began with deposition of formations A, B, and C, in that
forming nonconformity C. After E was deposited, a second body of order and one atop the other. This sequence was then cut by fault D.
magma F intruded across A , C , D , and E . Such an intrusive igneous After faulting, the land surface was eroded. When siltstone F was
body that is intruded along (parallel to) the strata is called a sill ( F ). deposited on the erosional surface, it became disconformity E.
Dating of Rocks, Fossils, and Geologic Events ■ 211