Page 54 - Materials Chemistry, Second Edition
P. 54
A N OVERVIEW OF THE LIFE CYCLE ASSESSMENT METHOD 35
Life-Cycle Sustainability Analysis (LCSA)
Goal and scope definition
Modeling
— Broadening the scope of indicators ·
Environmental
t \Multi-region IOA/general\
Eeon4my-wi<Je equilibrium models/..
10A/partial equilibrium
BOA/...
models/..
Process-LCA/EIO-LCA/ LCC SLCA
Product-oriented hybrid LCA
c Interpretation
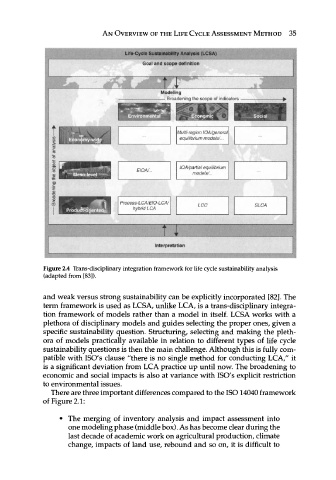
Figure 2.4 Trans-disciplinary integration framework for life cycle sustainability analysis
(adapted from [83]).
and weak versus strong sustainability can be explicitly incorporated [82]. The
term framework is used as LCSA, unlike LCA, is a trans-disciplinary integra-
tion framework of models rather than a model in itself. LCSA works with a
plethora of disciplinary models and guides selecting the proper ones, given a
specific sustainability question. Structuring, selecting and making the pleth-
ora of models practically available in relation to different types of life cycle
sustainability questions is then the main challenge. Although this is fully com-
patible with ISO's clause "there is no single method for conducting LCA," it
is a significant deviation from LCA practice up until now. The broadening to
economic and social impacts is also at variance with ISO's explicit restriction
to environmental issues.
There are three important differences compared to the ISO 14040 framework
of Figure 2.1:
• The merging of inventory analysis and impact assessment into
one modeling phase (middle box). As has become clear during the
last decade of academic work on agricultural production, climate
change, impacts of land use, rebound and so on, it is difficult to