Page 139 - Materials Chemistry, Second Edition
P. 139
Life Cycle Assessment of Biodiesel from Palm Oil 125
which are not transformed into any useful products. Emissions such as CO 2 ,N 2 O,
particulate matter are predominant in the transesterification stage.
On the whole, 2 % (Fig. 15) of the total environmental impacts were associated
with the transesterification stage with 1.36, 0.80, and 1.73 % of the total impacts
being assigned to human health, ecosystem depletion, and resource use,
respectively.
PME uses in diesel engine showed significance in acidification/eutrophication
potential due to the emission of CO 2 ,N 2 O, CO, and other particulate matter into
the environment. This stage offsets some of the environmental impacts by negating
them. Hence, the use of biodiesel contributed to the reduction of most of the
environmental impacts.
5.6 Emissions Associated with Transportation
Four main transportation stages were considered in this chapter, namely trans-
portation of oil palm seedlings to plantation site (T1), transportation of FFB from
plantation site to oil mill (T2), transportation of RPO to transesterification unit
(T3), and transportation of biodiesel to the consumer (T4). These stages contrib-
uted the most impacts (83 %) (Fig. 15) due to the use of fossil fuel which emitted
greenhouse gases and other particulate matter into the environment upon com-
bustion. The most significant impacts category associated with transportation is
climate change (Fig. 14). T1, T2, T3, and T4 contributed 5, 17, 43, and 19 % of
the total impacts associated with PME production, respectively. On the whole, all
the transportation stages contributed 71.33, 80.45, and 96.02 % to human health,
ecosystem depletion, and resource use, respectively.
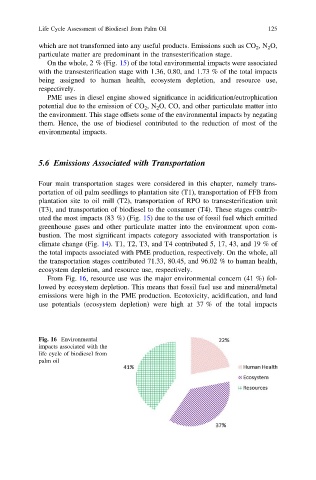
From Fig. 16, resource use was the major environmental concern (41 %) fol-
lowed by ecosystem depletion. This means that fossil fuel use and mineral/metal
emissions were high in the PME production. Ecotoxicity, acidification, and land
use potentials (ecosystem depletion) were high at 37 % of the total impacts
Fig. 16 Environmental
impacts associated with the
life cycle of biodiesel from
palm oil