Page 210 - Materials Chemistry, Second Edition
P. 210
198 E. Martínez Cámara et al.
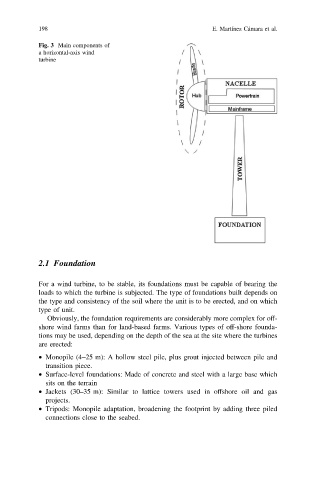
Fig. 3 Main components of
a horizontal-axis wind
turbine
2.1 Foundation
For a wind turbine, to be stable, its foundations must be capable of bearing the
loads to which the turbine is subjected. The type of foundations built depends on
the type and consistency of the soil where the unit is to be erected, and on which
type of unit.
Obviously, the foundation requirements are considerably more complex for off-
shore wind farms than for land-based farms. Various types of off-shore founda-
tions may be used, depending on the depth of the sea at the site where the turbines
are erected:
• Monopile (4–25 m): A hollow steel pile, plus grout injected between pile and
transition piece.
• Surface-level foundations: Made of concrete and steel with a large base which
sits on the terrain
• Jackets (30–35 m): Similar to lattice towers used in offshore oil and gas
projects.
• Tripods: Monopile adaptation, broadening the footprint by adding three piled
connections close to the seabed.