Page 30 - Materials Chemistry, Second Edition
P. 30
16 E. I. Wiloso and R. Heijungs
Mostly covered by LCA
Dietary trends Population
Less covered by LCA
Global food, Global energy Global fiber The least covered by LCA
feed demand demand demand
Food, feed, energy, fiber
Indirect production technology Indirect
resources emissions
Biomass production somewhere-else
(indirect agricultural land use) Energy supply and cost
Trade policy
Agricultural Land management Direct
practices policy resources
Production of biomass feedstocks Biomass Biomass Bioenergy Bioenergy
(direct agricultural land use) transport conversion distribution use
Direct
emissions
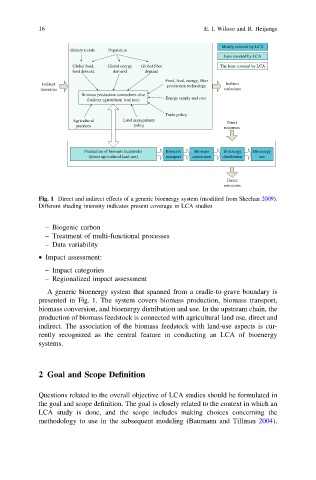
Fig. 1 Direct and indirect effects of a generic bioenergy system (modified from Sheehan 2009).
Different shading intensity indicates present coverage in LCA studies
– Biogenic carbon
– Treatment of multi-functional processes
– Data variability
• Impact assessment:
– Impact categories
– Regionalized impact assessment
A generic bioenergy system that spanned from a cradle-to-grave boundary is
presented in Fig. 1. The system covers biomass production, biomass transport,
biomass conversion, and bioenergy distribution and use. In the upstream chain, the
production of biomass feedstock is connected with agricultural land use, direct and
indirect. The association of the biomass feedstock with land-use aspects is cur-
rently recognized as the central feature in conducting an LCA of bioenergy
systems.
2 Goal and Scope Definition
Questions related to the overall objective of LCA studies should be formulated in
the goal and scope definition. The goal is closely related to the context in which an
LCA study is done, and the scope includes making choices concerning the
methodology to use in the subsequent modeling (Baumann and Tillman 2004).