Page 140 - Materials Chemistry, Second Edition
P. 140
136 6. Life cycle thinking for sustainable development in the building industry
Waste concrete
Recycled concrete
Recycle
Mortar
CDW treatment Recycled aggregate
company
Dregs
Lightweight block
Waste bricks
Waste wood
Reuse CDW treatment
Waste glass
company
Scrap metal
Solid waste
Reduce Building design
organization
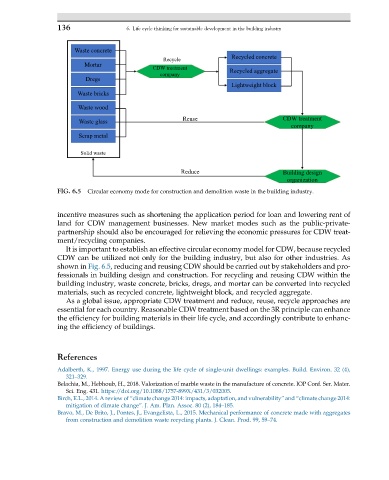
FIG. 6.5 Circular economy mode for construction and demolition waste in the building industry.
incentive measures such as shortening the application period for loan and lowering rent of
land for CDW management businesses. New market modes such as the public-private-
partnership should also be encouraged for relieving the economic pressures for CDW treat-
ment/recycling companies.
It is important to establish an effective circular economy model for CDW, because recycled
CDW can be utilized not only for the building industry, but also for other industries. As
shown in Fig. 6.5, reducing and reusing CDW should be carried out by stakeholders and pro-
fessionals in building design and construction. For recycling and reusing CDW within the
building industry, waste concrete, bricks, dregs, and mortar can be converted into recycled
materials, such as recycled concrete, lightweight block, and recycled aggregate.
As a global issue, appropriate CDW treatment and reduce, reuse, recycle approaches are
essential for each country. Reasonable CDW treatment based on the 3R principle can enhance
the efficiency for building materials in their life cycle, and accordingly contribute to enhanc-
ing the efficiency of buildings.
References
Adalberth, K., 1997. Energy use during the life cycle of single-unit dwellings: examples. Build. Environ. 32 (4),
321–329.
Belachia, M., Hebhoub, H., 2018. Valorization of marble waste in the manufacture of concrete. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater.
Sci. Eng. 431. https://doi.org/10.1088/1757-899X/431/3/032005.
Birch, E.L., 2014. A review of “climate change 2014: impacts, adaptation, and vulnerability” and “climate change 2014:
mitigation of climate change”. J. Am. Plan. Assoc. 80 (2), 184–185.
Bravo, M., De Brito, J., Pontes, J., Evangelista, L., 2015. Mechanical performance of concrete made with aggregates
from construction and demolition waste recycling plants. J. Clean. Prod. 99, 59–74.