Page 15 - Materials Chemistry, Second Edition
P. 15
1.4 Tools and actions in LCT 9
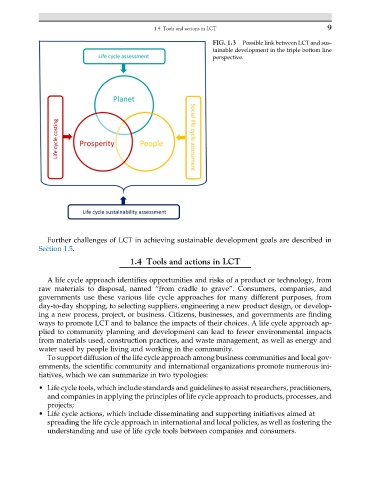
FIG. 1.3 Possible link between LCT and sus-
tainable development in the triple bottom line
perspective.
Further challenges of LCT in achieving sustainable development goals are described in
Section 1.5.
1.4 Tools and actions in LCT
A life cycle approach identifies opportunities and risks of a product or technology, from
raw materials to disposal, named “from cradle to grave”. Consumers, companies, and
governments use these various life cycle approaches for many different purposes, from
day-to-day shopping, to selecting suppliers, engineering a new product design, or develop-
ing a new process, project, or business. Citizens, businesses, and governments are finding
ways to promote LCT and to balance the impacts of their choices. A life cycle approach ap-
plied to community planning and development can lead to fewer environmental impacts
from materials used, construction practices, and waste management, as well as energy and
water used by people living and working in the community.
To support diffusion of the life cycle approach among business communities and local gov-
ernments, the scientific community and international organizations promote numerous ini-
tiatives, which we can summarize in two typologies:
• Life cycle tools, which include standards and guidelines to assist researchers, practitioners,
and companies in applying the principles of life cycle approach to products, processes, and
projects;
• Life cycle actions, which include disseminating and supporting initiatives aimed at
spreading the life cycle approach in international and local policies, as well as fostering the
understanding and use of life cycle tools between companies and consumers.