Page 30 - Lindens Handbook of Batteries
P. 30
BASIC CONCEPTS 1.7
Electron flow
Load
– +
Flow of anions
Anode Cathode
Flow of cations
Electrolyte
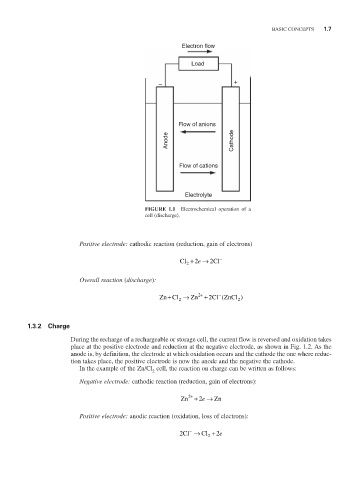
FIGURE 1.1 Electrochemical operation of a
cell (discharge).
Positive electrode: cathodic reaction (reduction, gain of electrons)
Cl + 2 → e 2 Cl −
2
Overall reaction (discharge):
−
+
2
+
Zn Cl → Zn + 2 Cl ZnCl )
(
2 2
1.3.2 Charge
During the recharge of a rechargeable or storage cell, the current flow is reversed and oxidation takes
place at the positive electrode and reduction at the negative electrode, as shown in Fig. 1.2. As the
anode is, by definition, the electrode at which oxidation occurs and the cathode the one where reduc-
tion takes place, the positive electrode is now the anode and the negative the cathode.
In the example of the Zn/Cl cell, the reaction on charge can be written as follows:
2
Negative electrode: cathodic reaction (reduction, gain of electrons):
Zn + 2+ 2 → e Zn
Positive electrode: anodic reaction (oxidation, loss of electrons):
2Cl → − Cl + 2e
2