Page 12 - MATLAB Recipes for Earth Sciences
P. 12
2 1 Data Analysis in Earth Sciences
1. the sample size – This parameter includes the sample volume or its weight
as well as the number of samples collected in the field. The rock weight
or volume can be a critical factor if the samples are later analyzed in the
laboratory. On the application of certain analytic techniques a specifi c
amount of material may be required. The sample size also restricts the
number of subsamples that eventually could be collected from the single
sample. If the population is heterogeneous, then the sample needs to be
large enough to represent the population·s variability. On the other hand,
a sample should always be as small as possible in order to save time and
effort to analyze it. It is recommended to collect a smaller pilot sample
before defining a suitable sample size.
Hypothetical Accessible
Population Population
Outcrop
Geological
sample
Road cut
Available
Population
River valley
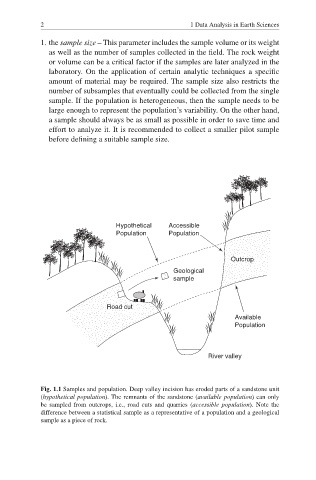
Fig. 1.1 Samples and population. Deep valley incision has eroded parts of a sandstone unit
(hypothetical population). The remnants of the sandstone ( available population) can only
be sampled from outcrops, i.e., road cuts and quarries ( accessible population). Note the
difference between a statistical sample as a representative of a population and a geological
sample as a piece of rock.