Page 188 - Machine Learning for Subsurface Characterization
P. 188
Dimensionality reduction and clustering techniques Chapter 6 163
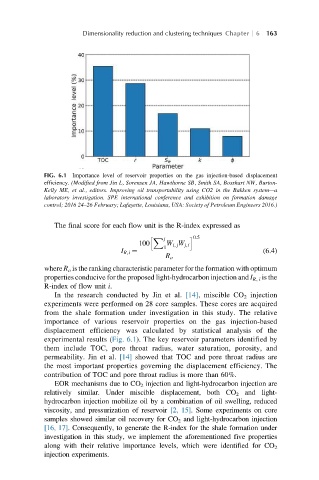
FIG. 6.1 Importance level of reservoir properties on the gas injection-based displacement
efficiency. (Modified from Jin L, Sorensen JA, Hawthorne SB, Smith SA, Bosshart NW, Burton-
Kelly ME, et al., editors. Improving oil transportability using CO2 in the Bakken system—a
laboratory investigation. SPE international conference and exhibition on formation damage
control; 2016 24–26 February; Lafayette, Louisiana, USA: Society of Petroleum Engineers 2016.)
The final score for each flow unit is the R-index expressed as
h i 0:5
X j
100 W i, j W j,i
1
I R,i ¼ (6.4)
R o
where R o is the ranking characteristic parameter for the formation with optimum
properties conducive for the proposed light-hydrocarbon injection and I R, i is the
R-index of flow unit i.
In the research conducted by Jin et al. [14],miscibleCO 2 injection
experiments were performed on 28 core samples. These cores are acquired
from the shale formation under investigation in this study. The relative
importance of various reservoir properties on the gas injection-based
displacement efficiency was calculated by statistical analysis of the
experimental results (Fig. 6.1). The key reservoir parameters identified by
them include TOC, pore throat radius, water saturation, porosity, and
permeability. Jin et al. [14] showed that TOC and pore throat radius are
the most important properties governing the displacement efficiency. The
contribution of TOC and pore throat radius is more than 60%.
EOR mechanisms due to CO 2 injection and light-hydrocarbon injection are
relatively similar. Under miscible displacement, both CO 2 and light-
hydrocarbon injection mobilize oil by a combination of oil swelling, reduced
viscosity, and pressurization of reservoir [2, 15]. Some experiments on core
samples showed similar oil recovery for CO 2 and light-hydrocarbon injection
[16, 17]. Consequently, to generate the R-index for the shale formation under
investigation in this study, we implement the aforementioned five properties
along with their relative importance levels, which were identified for CO 2
injection experiments.