Page 242 -
P. 242
Chapter 6 Foundations of Business Intelligence: Databases and Information Management 241
6.1 ORGANIZING DATA IN A TRADITIONAL FILE
ENVIRONMENT
A n effective information system provides users with accurate, timely,
and relevant information. Accurate information is free of errors.
Information is timely when it is available to decision makers when it
is needed. Information is relevant when it is useful and appropriate
for the types of work and decisions that require it.
You might be surprised to learn that many businesses don’t have timely,
accurate, or relevant information because the data in their information systems
have been poorly organized and maintained. That’s why data management is
so essential. To understand the problem, let’s look at how information systems
arrange data in computer files and traditional methods of file management.
FILE ORGANIZATION TERMS AND CONCEPTS
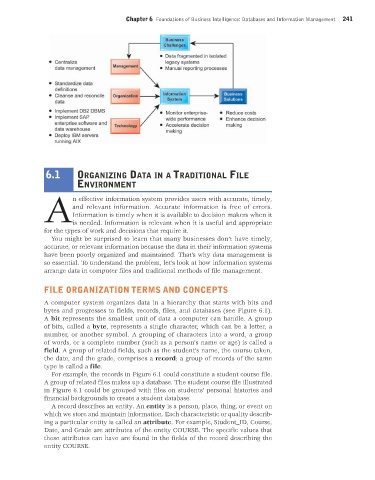
A computer system organizes data in a hierarchy that starts with bits and
bytes and progresses to fields, records, files, and databases (see Figure 6.1).
A bit represents the smallest unit of data a computer can handle. A group
of bits, called a byte, represents a single character, which can be a letter, a
number, or another symbol. A grouping of characters into a word, a group
of words, or a complete number (such as a person’s name or age) is called a
field. A group of related fields, such as the student’s name, the course taken,
the date, and the grade, comprises a record; a group of records of the same
type is called a file.
For example, the records in Figure 6.1 could constitute a student course file.
A group of related files makes up a database. The student course file illustrated
in Figure 6.1 could be grouped with files on students’ personal histories and
financial backgrounds to create a student database.
A record describes an entity. An entity is a person, place, thing, or event on
which we store and maintain information. Each characteristic or quality describ-
ing a particular entity is called an attribute. For example, Student_ID, Course,
Date, and Grade are attributes of the entity COURSE. The specific values that
these attributes can have are found in the fields of the record describing the
entity COURSE.
MIS_13_Ch_06 Global.indd 241 1/17/2013 2:27:40 PM