Page 43 - Managing Change in Organizations
P. 43
CarnCh02v3.qxd 3/30/07 4:09 PM Page 26
Chapter 2 ■ Organization structures: choice and leadership
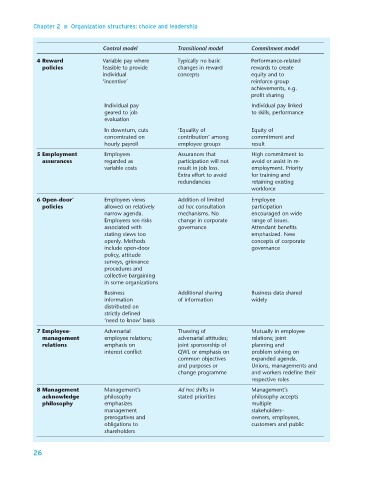
Control model Transitional model Commitment model
4 Reward Variable pay where Typically no basic Performance-related
policies feasible to provide changes in reward rewards to create
individual concepts equity and to
‘incentive’ reinforce group
achievements, e.g.
profit sharing
Individual pay Individual pay linked
geared to job to skills, performance
evaluation
In downturn, cuts ‘Equality of Equity of
concentrated on contribution’ among commitment and
hourly payroll employee groups result
5 Employment Employees Assurances that High commitment to
assurances regarded as participation will not avoid or assist in re-
variable costs result in job loss. employment. Priority
Extra effort to avoid for training and
redundancies retaining existing
workforce
6 Open-door’ Employees views Addition of limited Employee
policies allowed on relatively ad hoc consultation participation
narrow agenda. mechanisms. No encouraged on wide
Employees see risks change in corporate range of issues.
associated with governance Attendant benefits
stating views too emphasized. New
openly. Methods concepts of corporate
include open-door governance
policy, attitude
surveys, grievance
procedures and
collective bargaining
in some organizations
Business Additional sharing Business data shared
information of information widely
distributed on
strictly defined
‘need to know’ basis
7 Employee- Adversarial Thawing of Mutually in employee
management employee relations; adversarial attitudes; relations; joint
relations emphasis on joint sponsorship of planning and
interest conflict QWL or emphasis on problem solving on
common objectives expanded agenda.
and purposes or Unions, managements and
change programme and workers redefine their
respective roles
8 Management Management’s Ad hoc shifts in Management’s
acknowledge philosophy stated priorities philosophy accepts
philosophy emphasizes multiple
management stakeholders–
prerogatives and owners, employees,
obligations to customers and public
shareholders
26