Page 194 - Managing Global Warming
P. 194
156 Managing Global Warming
As a new approach, the latest GFR concept will have the indirect cycle. A heat
exchanger transfers the heat from the primary helium coolant to a secondary gas cycle
containing a helium-nitrogen mixture, which in turn drives a closed-cycle gas turbine.
The waste heat from the gas-turbine exhaust is used to raise steam in a steam gener-
ator, which is then used to drive a steam turbine. Such a combined cycle is common
practice in natural gas-fired power plants, so it represents an established technology,
with the only difference in the GFR case being the use of a closed-cycle gas turbine.
4.3.5.3 Sodium-cooled fast reactor
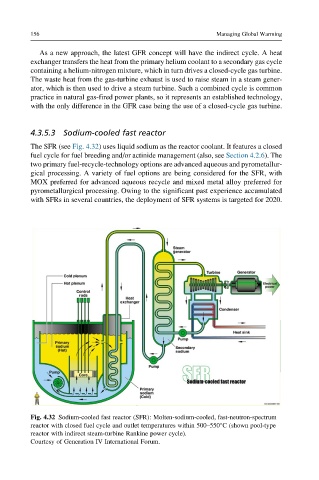
The SFR (see Fig. 4.32) uses liquid sodium as the reactor coolant. It features a closed
fuel cycle for fuel breeding and/or actinide management (also, see Section 4.2.6). The
two primary fuel-recycle-technology options are advanced aqueous and pyrometallur-
gical processing. A variety of fuel options are being considered for the SFR, with
MOX preferred for advanced aqueous recycle and mixed metal alloy preferred for
pyrometallurgical processing. Owing to the significant past experience accumulated
with SFRs in several countries, the deployment of SFR systems is targeted for 2020.
Fig. 4.32 Sodium-cooled fast reactor (SFR): Molten-sodium-cooled, fast-neutron-spectrum
reactor with closed fuel cycle and outlet temperatures within 500–550°C (shown pool-type
reactor with indirect steam-turbine Rankine power cycle).
Courtesy of Generation IV International Forum.