Page 29 - Master Handbook of Acoustics
P. 29
affects the velocity of sound in air; the more humid the air, the faster the speed. It should be noted that
the speed (velocity) of sound is different from the particle velocity. The speed (velocity) of sound
determines how fast sound energy moves across a medium. Particle velocity is determined by the
loudness of the sound.
Wavelength and Frequency
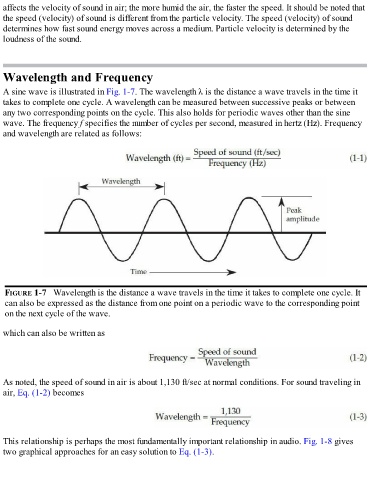
A sine wave is illustrated in Fig. 1-7. The wavelength λ is the distance a wave travels in the time it
takes to complete one cycle. A wavelength can be measured between successive peaks or between
any two corresponding points on the cycle. This also holds for periodic waves other than the sine
wave. The frequency f specifies the number of cycles per second, measured in hertz (Hz). Frequency
and wavelength are related as follows:
FIGURE 1-7 Wavelength is the distance a wave travels in the time it takes to complete one cycle. It
can also be expressed as the distance from one point on a periodic wave to the corresponding point
on the next cycle of the wave.
which can also be written as
As noted, the speed of sound in air is about 1,130 ft/sec at normal conditions. For sound traveling in
air, Eq. (1-2) becomes
This relationship is perhaps the most fundamentally important relationship in audio. Fig. 1-8 gives
two graphical approaches for an easy solution to Eq. (1-3).