Page 57 - Master Handbook of Acoustics
P. 57
across the audio band. For example, our hearing sensitivity particularly rolls off at low frequencies,
and also at high frequencies. Moreover, this roll-off is more pronounced at softer listening levels. For
this reason, to emulate human hearing, sound level meters usually offer a selection of weighting
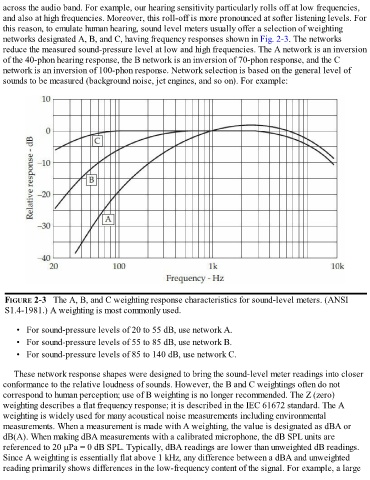
networks designated A, B, and C, having frequency responses shown in Fig. 2-3. The networks
reduce the measured sound-pressure level at low and high frequencies. The A network is an inversion
of the 40-phon hearing response, the B network is an inversion of 70-phon response, and the C
network is an inversion of 100-phon response. Network selection is based on the general level of
sounds to be measured (background noise, jet engines, and so on). For example:
FIGURE 2-3 The A, B, and C weighting response characteristics for sound-level meters. (ANSI
S1.4-1981.) A weighting is most commonly used.
• For sound-pressure levels of 20 to 55 dB, use network A.
• For sound-pressure levels of 55 to 85 dB, use network B.
• For sound-pressure levels of 85 to 140 dB, use network C.
These network response shapes were designed to bring the sound-level meter readings into closer
conformance to the relative loudness of sounds. However, the B and C weightings often do not
correspond to human perception; use of B weighting is no longer recommended. The Z (zero)
weighting describes a flat frequency response; it is described in the IEC 61672 standard. The A
weighting is widely used for many acoustical noise measurements including environmental
measurements. When a measurement is made with A weighting, the value is designated as dBA or
dB(A). When making dBA measurements with a calibrated microphone, the dB SPL units are
referenced to 20 μPa = 0 dB SPL. Typically, dBA readings are lower than unweighted dB readings.
Since A weighting is essentially flat above 1 kHz, any difference between a dBA and unweighted
reading primarily shows differences in the low-frequency content of the signal. For example, a large