Page 182 - Materials Chemistry, Second Edition
P. 182
169
3.1. Mining and Processing of Metals
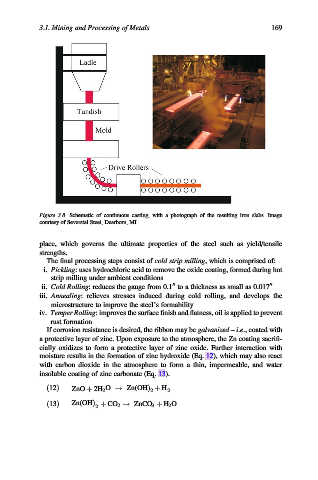
Figure 3.8. Schematic of continuous casting, with a photograph of the resulting iron slabs. Image
courtesy of Severstal Steel, Dearborn, MI.
place, which governs the ultimate properties of the steel such as yield/tensile
strengths.
The final processing steps consist of cold strip milling, which is comprised of:
i. Pickling: uses hydrochloric acid to remove the oxide coating, formed during hot
strip milling under ambient conditions
ii. Cold Rolling: reduces the gauge from 0.1 to a thickness as small as 0.017 00
00
iii. Annealing: relieves stresses induced during cold rolling, and develops the
microstructure to improve the steel’s formability
iv. Temper Rolling: improves the surface finish and flatness, oil is applied to prevent
rust formation
If corrosion resistance is desired, the ribbon may be galvanized – i.e., coated with
a protective layer of zinc. Upon exposure to the atmosphere, the Zn coating sacrifi-
cially oxidizes to form a protective layer of zinc oxide. Further interaction with
moisture results in the formation of zinc hydroxide (Eq. 12), which may also react
with carbon dioxide in the atmosphere to form a thin, impermeable, and water
insoluble coating of zinc carbonate (Eq. 13).
ð12Þ ZnO þ 2H 2 O ! Zn(OHÞ þ H 2
2
ð13Þ Zn(OHÞ þ CO 2 ! ZnCO 3 þ H 2 O
2