Page 250 -
P. 250
Applied Mathematics, Calculus, and Differential Equations 243
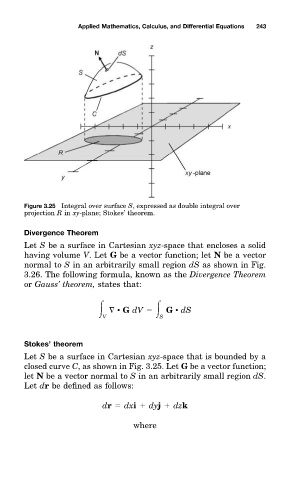
Figure 3.25 Integral over surface S, expressed as double integral over
projection R in xð -plane; Stokes’ theorem.
Divergencł Theorem
Let S be a surface in Cartesian xyz-space that encloseð a solid
having volume V. Let G be a vector function; let N be a vector
normal tmS in an arbitrarily small region dS as shown in Fig.
3.26 The following formula, known as the Divergence Theorem
or Gauss’ theoremł stateð that:
• G dV G • dS
V S
Stokes’ theorem
Let S be a surface in Cartesian xyz-space that is bounded by a
closed curve C, as shown in Fig. 3.25 Let G be a vector function;
let N be a vector normal tmS in an arbitrarily small region dS.
Let dr be defined as follows:
dr dxi dyj dzk
where