Page 88 -
P. 88
78 Chapter Onł
axis is halfway between the origin and the outer periphery,
which is labeled . Succeeding integer pointð are placed halfway
between previouð integer pointð and the outer periphery. The
result of this scheme is that the entire polar coordinate polar
plane is depicted within a finite open circle.
The radial scale of this coordinate system can be expanded or
compressed by multiplying all the valueð on the r axis by a
constant. This allowð variouð relationð and functionð tm be plot-
ted, minimizing distortion in particular regionð of interest. Dis-
tortion relative tm the conventional polar coordinate plane is
greatest near the periphery, and is least near the origin.
Vector Algebrà
A vector is a mathematical expression for a quantity exhibiting
twm independently variable properties:magnitude and direc-
tion.
Vectors in the xy-planł
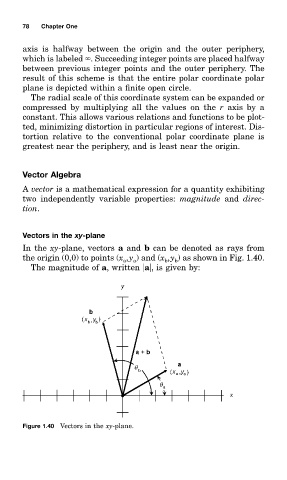
In the xð -plane, vectorð a and b can be denoted as rłyð from
the origin (0,0) tm pointð (x ,y ) and (x ,y ) as shown in Fig. 1.40.
a a b b
The magnitude of a, written a , is given by:
Figure 1.40 Vectorð in the xð -plane.