Page 82 - Mechanical Behavior of Materials
P. 82
Section 3.4 Nonferrous Metals 81
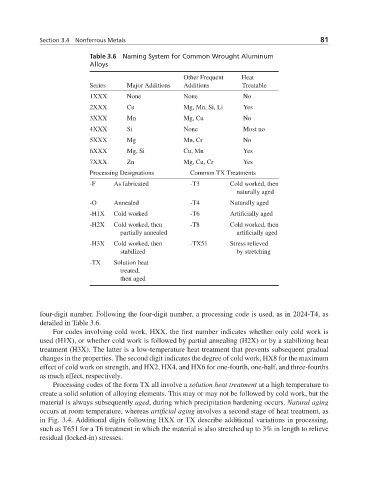
Table 3.6 Naming System for Common Wrought Aluminum
Alloys
Other Frequent Heat
Series Major Additions Additions Treatable
1XXX None None No
2XXX Cu Mg,Mn, Si,Li Yes
3XXX Mn Mg, Cu No
4XXX Si None Most no
5XXX Mg Mn, Cr No
6XXX Mg, Si Cu, Mn Yes
7XXX Zn Mg, Cu, Cr Yes
Processing Designations Common TX Treatments
-F As fabricated -T3 Cold worked, then
naturally aged
-O Annealed -T4 Naturally aged
-H1X Cold worked -T6 Artificially aged
-H2X Cold worked, then -T8 Cold worked, then
partially annealed artificially aged
-H3X Cold worked, then -TX51 Stress relieved
stabilized by stretching
-TX Solution heat
treated,
then aged
four-digit number. Following the four-digit number, a processing code is used, as in 2024-T4, as
detailed in Table 3.6.
For codes involving cold work, HXX, the first number indicates whether only cold work is
used (H1X), or whether cold work is followed by partial annealing (H2X) or by a stabilizing heat
treatment (H3X). The latter is a low-temperature heat treatment that prevents subsequent gradual
changes in the properties. The second digit indicates the degree of cold work, HX8 for the maximum
effect of cold work on strength, and HX2, HX4, and HX6 for one-fourth, one-half, and three-fourths
as much effect, respectively.
Processing codes of the form TX all involve a solution heat treatment at a high temperature to
create a solid solution of alloying elements. This may or may not be followed by cold work, but the
material is always subsequently aged, during which precipitation hardening occurs. Natural aging
occurs at room temperature, whereas artificial aging involves a second stage of heat treatment, as
in Fig. 3.4. Additional digits following HXX or TX describe additional variations in processing,
such as T651 for a T6 treatment in which the material is also stretched up to 3% in length to relieve
residual (locked-in) stresses.