Page 272 - Mechanical Engineers' Handbook (Volume 2)
P. 272
2 The System Life Cycle and Functional Elements of Systems Engineering 263
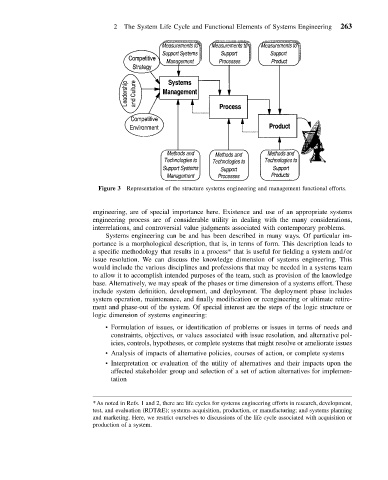
Figure 3 Representation of the structure systems engineering and management functional efforts.
engineering, are of special importance here. Existence and use of an appropriate systems
engineering process are of considerable utility in dealing with the many considerations,
interrelations, and controversial value judgments associated with contemporary problems.
Systems engineering can be and has been described in many ways. Of particular im-
portance is a morphological description, that is, in terms of form. This description leads to
a specific methodology that results in a process* that is useful for fielding a system and/or
issue resolution. We can discuss the knowledge dimension of systems engineering. This
would include the various disciplines and professions that may be needed in a systems team
to allow it to accomplish intended purposes of the team, such as provision of the knowledge
base. Alternatively, we may speak of the phases or time dimension of a systems effort. These
include system definition, development, and deployment. The deployment phase includes
system operation, maintenance, and finally modification or reengineering or ultimate retire-
ment and phase-out of the system. Of special interest are the steps of the logic structure or
logic dimension of systems engineering:
• Formulation of issues, or identification of problems or issues in terms of needs and
constraints, objectives, or values associated with issue resolution, and alternative pol-
icies, controls, hypotheses, or complete systems that might resolve or ameliorate issues
• Analysis of impacts of alternative policies, courses of action, or complete systems
• Interpretation or evaluation of the utility of alternatives and their impacts upon the
affected stakeholder group and selection of a set of action alternatives for implemen-
tation
*As noted in Refs. 1 and 2, there are life cycles for systems engineering efforts in research, development,
test, and evaluation (RDT&E); systems acquisition, production, or manufacturing; and systems planning
and marketing. Here, we restrict ourselves to discussions of the life cycle associated with acquisition or
production of a system.