Page 311 - Mechanical Engineers' Handbook (Volume 2)
P. 311
302 Mathematical Models of Dynamic Physical Systems
directly into the simulation, replacing the corresponding model components. An iterative,
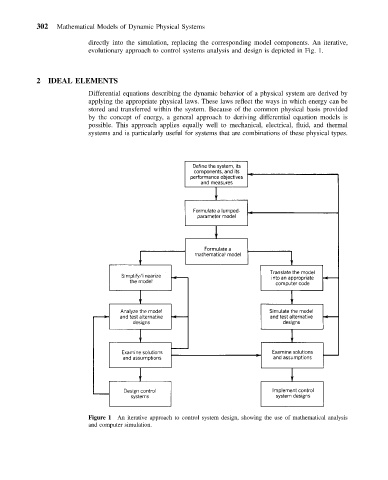
evolutionary approach to control systems analysis and design is depicted in Fig. 1.
2 IDEAL ELEMENTS
Differential equations describing the dynamic behavior of a physical system are derived by
applying the appropriate physical laws. These laws reflect the ways in which energy can be
stored and transferred within the system. Because of the common physical basis provided
by the concept of energy, a general approach to deriving differential equation models is
possible. This approach applies equally well to mechanical, electrical, fluid, and thermal
systems and is particularly useful for systems that are combinations of these physical types.
Figure 1 An iterative approach to control system design, showing the use of mathematical analysis
and computer simulation.