Page 707 - Mechanical Engineers' Handbook (Volume 2)
P. 707
698 General-Purpose Control Devices
programs are transferred through a ‘‘drip-feed’’ technique where the CNC runs the program
as the program is downloaded from the DNC.
Numerical controllers are widely used in industry today. The predominant application
of NC is still for metal-cutting machine tools. Some of the basic operations performed by
machine tools in metal machining are turning, boring, drilling, facing, forming, milling,
shaping, and planing. 16 Turning is one of the most common operations in metal cutting.
Turning is usually accomplished by lathe machines. The part or workpiece is secured in the
chuck of a lathe machine and rotated. The tool, held rigidly in a tool post, is moved at a
constant speed along the rotational axis of the workpiece, cutting away a layer of metal to
form a cylinder or a surface of a more complex profile.
Applications other than metal machining for numerical controllers include flame cutting,
water jet cutting, plasma arc cutting, laser beam cutting, spot and arc welding, and assembly
machines. 17
3.2 Principles of Operation
NC System Components
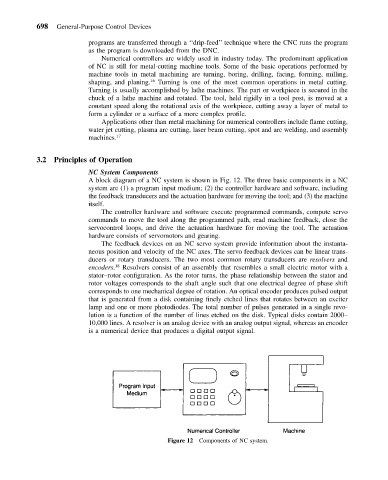
A block diagram of a NC system is shown in Fig. 12. The three basic components in a NC
system are (1) a program input medium; (2) the controller hardware and software, including
the feedback transducers and the actuation hardware for moving the tool; and (3) the machine
itself.
The controller hardware and software execute programmed commands, compute servo
commands to move the tool along the programmed path, read machine feedback, close the
servocontrol loops, and drive the actuation hardware for moving the tool. The actuation
hardware consists of servomotors and gearing.
The feedback devices on an NC servo system provide information about the instanta-
neous position and velocity of the NC axes. The servo feedback devices can be linear trans-
ducers or rotary transducers. The two most common rotary transducers are resolvers and
encoders. 18 Resolvers consist of an assembly that resembles a small electric motor with a
stator–rotor configuration. As the rotor turns, the phase relationship between the stator and
rotor voltages corresponds to the shaft angle such that one electrical degree of phase shift
corresponds to one mechanical degree of rotation. An optical encoder produces pulsed output
that is generated from a disk containing finely etched lines that rotates between an exciter
lamp and one or more photodiodes. The total number of pulses generated in a single revo-
lution is a function of the number of lines etched on the disk. Typical disks contain 2000–
10,000 lines. A resolver is an analog device with an analog output signal, whereas an encoder
is a numerical device that produces a digital output signal.
Figure 12 Components of NC system.