Page 111 - Mechanical Engineers' Handbook (Volume 4)
P. 111
100 Thermodynamics Fundamentals
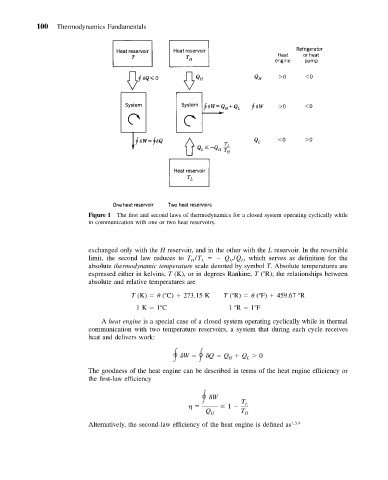
Figure 1 The first and second laws of thermodynamics for a closed system operating cyclically while
in communication with one or two heat reservoirs.
exchanged only with the H reservoir, and in the other with the L reservoir. In the reversible
limit, the second law reduces to T /T Q /Q , which serves as definition for the
L
H
H
L
absolute thermodynamic temperature scale denoted by symbol T. Absolute temperatures are
expressed either in kelvins, T (K), or in degrees Rankine, T ( R); the relationships between
absolute and relative temperatures are
T (K) ( C) 273.15 K T ( R) ( F) 459.67 R
1K 1 C 1 R 1 F
A heat engine is a special case of a closed system operating cyclically while in thermal
communication with two temperature reservoirs, a system that during each cycle receives
heat and delivers work:
W Q Q Q 0
H L
The goodness of the heat engine can be described in terms of the heat engine efficiency or
the first-law efficiency
W
1 T L
Q H T H
Alternatively, the second-law efficiency of the heat engine is defined as 1,3,4