Page 189 - Mechanical Engineers' Handbook (Volume 4)
P. 189
178 Heat-Transfer Fundamentals
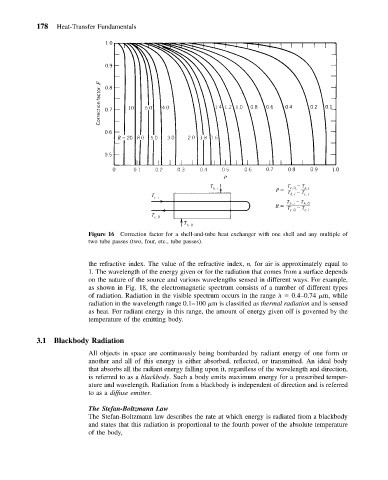
Figure 16 Correction factor for a shell-and-tube heat exchanger with one shell and any multiple of
two tube passes (two, four, etc., tube passes).
the refractive index. The value of the refractive index, n, for air is approximately equal to
1. The wavelength of the energy given or for the radiation that comes from a surface depends
on the nature of the source and various wavelengths sensed in different ways. For example,
as shown in Fig. 18, the electromagnetic spectrum consists of a number of different types
of radiation. Radiation in the visible spectrum occurs in the range 0.4–0.74 m, while
radiation in the wavelength range 0.1–100 m is classified as thermal radiation and is sensed
as heat. For radiant energy in this range, the amount of energy given off is governed by the
temperature of the emitting body.
3.1 Blackbody Radiation
All objects in space are continuously being bombarded by radiant energy of one form or
another and all of this energy is either absorbed, reflected, or transmitted. An ideal body
that absorbs all the radiant energy falling upon it, regardless of the wavelength and direction,
is referred to as a blackbody. Such a body emits maximum energy for a prescribed temper-
ature and wavelength. Radiation from a blackbody is independent of direction and is referred
to as a diffuse emitter.
The Stefan-Boltzmann Law
The Stefan-Boltzmann law describes the rate at which energy is radiated from a blackbody
and states that this radiation is proportional to the fourth power of the absolute temperature
of the body,