Page 238 - Mechanical Engineers' Handbook (Volume 4)
P. 238
8 Heat Transfer 227
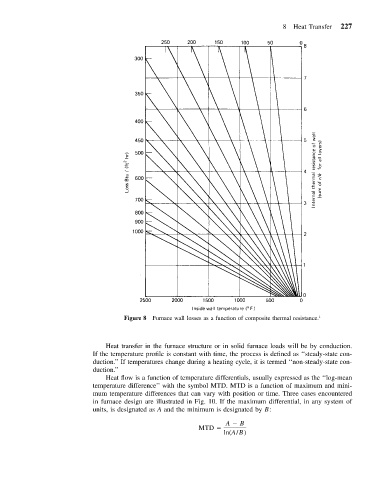
Figure 8 Furnace wall losses as a function of composite thermal resistance. 1
Heat transfer in the furnace structure or in solid furnace loads will be by conduction.
If the temperature profile is constant with time, the process is defined as ‘‘steady-state con-
duction.’’ If temperatures change during a heating cycle, it is termed ‘‘non-steady-state con-
duction.’’
Heat flow is a function of temperature differentials, usually expressed as the ‘‘log-mean
temperature difference’’ with the symbol MTD. MTD is a function of maximum and mini-
mum temperature differences that can vary with position or time. Three cases encountered
in furnace design are illustrated in Fig. 10. If the maximum differential, in any system of
units, is designated as A and the minimum is designated by B:
A B
MTD
ln(A/B)