Page 252 - Membranes for Industrial Wastewater Recovery and Re-Use
P. 252
System design aids 22 1
4.3.4 Problem in electrodialysis: energy demand
A light brackish water of the specijication below requires demineralisation using a
500 cell pair, 7 x 0.75 rn electrodialysis stack for potable water production: Na+,
830 ppm; Cl-, 1530 ppm; Ca2", 100 ppm, S042 , 50 ppm; Mg2+, 60 ppni; HC03-,
120 ppm.
It is desired that the sodium content be halved. If the ED softens at twice the rate of
desalination according to first order kinetics, and the process operates with an overall
current eficiency of 95% calculate (a) the total current required, and (b) the specific
energy demand in kWh rnP3 for a conversion of 8.5% and an average production rate of
500 rn3/day desalinated water. How would the specific energy demand change if a
further stage were added to yielda 75% desalinatedproduct?
Assume specific cell pair area resistance is given by: r (ohms cm2) = IO + (1 04/
C,,,,), C,,, being the average concentration in meq 1-'of the diluate stream passing
through the stack.
Solution
Electrodialysis demands a knowledge of the concentration of charge, since this
can be directly related to the current demanded by the Faraday equation. Thus
all concentrations must be converted to meq/l by dividing by the molar weight
and multiplying by the charge:
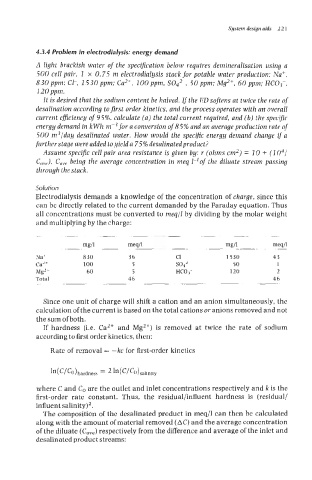
-- mg/l mdl mg/l m g
Na' 830 36 CI 1530 43
CaL+ 100 5 so42 50 1
Mg2+ 60 5 HC03- 120 -
7
Total 46 46
-
Since one unit of charge will shift a cation and an anion simultaneously, the
calculation of the current is based on the total cations or anions removed and not
the sum of both.
If hardness (i.e. Ca2+ and Mg2+) is removed at twice the rate of sodium
according to first order kinetics, then:
Rate of removal = -kc for first-order kinetics
where C and Co are the outlet and inlet concentrations respectively and k is the
first-order rate constant. Thus, the residual/influent hardness is (residual/
influent salinity)2.
The composition of the desalinated product in meq/l can then be calculated
along with the amount of material removed (AC) and the average concentration
of the diluate (Cave) respectively from the difference and average of the inlet and
desalinated product streams: