Page 20 - Methods For Monitoring And Diagnosing The Efficiency Of Catalytic Converters A Patent - oriented Survey
P. 20
Introduction 3
I .7 g/mile (1.062 &m) CO
0.2 g/mile (0.125 dkm) NO,
California has even stricter laws. For example, non-methane HC emissions (NMHC) must be
0.075 g/mile (0.046 g/km) by 2000 in 96% of all cars. Through the remainder of the 1990s,
California law stipulates standards for Transitional Low Emission Vehicles (TLEV), Low
Emission Vehicles (LEV) and for Ultra Low Emission Vehicles (ULEV) (see [3], and [4]).
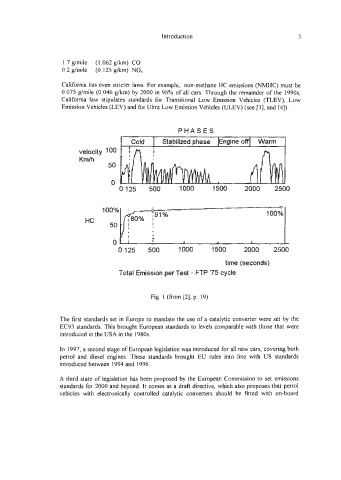
PHASES
velocity 100
Km/h
50
0
0 125 500 1000 1500 2000 2500
1 ~ ; ; - ~ % 0 0 1 I 80% 100%
HC 50
1 *
!
0
0 125 500 1000 1500 2000 2500
time (seconds)
Total Emission per Test - FTP '75 cycle
Fig. 1 (from [2], p. 19)
The first standards set in Europe to mandate the use of a catalytic converter were set by the
EC93 standards. This brought European standards to levels comparable with those that were
introduced in the USA in the 1980s.
In 1997, a second stage of European legislation was introduced for all new cars, covering both
petrol and diesel engines. These standards brought EU rules into line with US standards
introduced between 1994 and 1996.
A third state of legislation has been proposed by the European Commission to set emissions
standards for 2000 and beyond. It comes as a draft directive, which also proposes that petrol
vehicles with electronically controlled catalytic converters should be fitted with on-board