Page 88 - Microsoft Office Excel 2003 Programming Inside Out
P. 88
Microsoft Office Excel 2003 Programming Inside Out
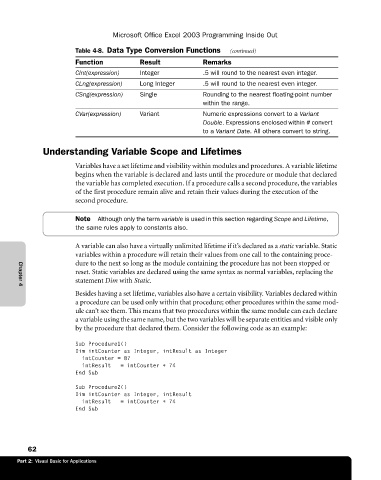
Table 4-8. Data Type Conversion Functions (continued)
Function Result Remarks
CInt(expression) Integer .5 will round to the nearest even integer.
CLng(expression) Long Integer .5 will round to the nearest even integer.
CSng(expression) Single Rounding to the nearest floating-point number
within the range.
CVar(expression) Variant Numeric expressions convert to a Variant
Double. Expressions enclosed within # convert
to a Variant Date. All others convert to string.
Understanding Variable Scope and Lifetimes
Variables have a set lifetime and visibility within modules and procedures. A variable lifetime
begins when the variable is declared and lasts until the procedure or module that declared
the variable has completed execution. If a procedure calls a second procedure, the variables
of the first procedure remain alive and retain their values during the execution of the
second procedure.
Note Although only the term variable is used in this section regarding Scope and Lifetime,
the same rules apply to constants also.
A variable can also have a virtually unlimited lifetime if it’s declared as a static variable. Static
variables within a procedure will retain their values from one call to the containing proce
dure to the next so long as the module containing the procedure has not been stopped or
reset. Static variables are declared using the same syntax as normal variables, replacing the
statement Dim with Static.
Chapter 4
Besides having a set lifetime, variables also have a certain visibility. Variables declared within
a procedure can be used only within that procedure; other procedures within the same mod
ule can’t see them. This means that two procedures within the same module can each declare
a variable using the same name, but the two variables will be separate entities and visible only
by the procedure that declared them. Consider the following code as an example:
Sub Procedure1()
Dim intCounter as Integer, intResult as Integer
intCounter = 87
intResult = intCounter * 74
End Sub
Sub Procedure2()
Dim intCounter as Integer, intResult
intResult = intCounter * 74
End Sub
62
Part 2: Visual Basic for Applications