Page 20 - Mobile Data Loss
P. 20
14 Mobile Data Loss
Man-in-the- Corporate
Middle
Intruder
Active
Directory
Mobile device
Certs
Evil Twin AP
SSID = CoffeeShop
Email
Apps
Content
X
Deauth/Disassociate
Packet
SSID = CoffeeShop
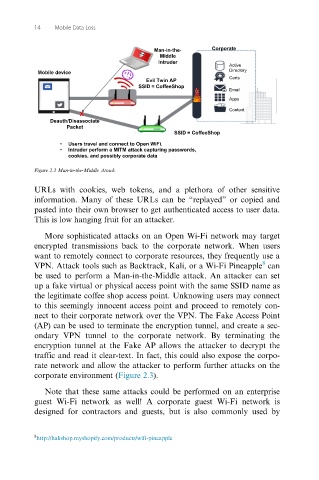
• Users travel and connect to Open WiFi.
• Intruder perform a MITM attack capturing passwords,
cookies, and possibly corporate data
Figure 2.3 Man-in-the-Middle Attack.
URLs with cookies, web tokens, and a plethora of other sensitive
information. Many of these URLs can be “replayed” or copied and
pasted into their own browser to get authenticated access to user data.
This is low hanging fruit for an attacker.
More sophisticated attacks on an Open Wi-Fi network may target
encrypted transmissions back to the corporate network. When users
want to remotely connect to corporate resources, they frequently use a
8
VPN. Attack tools such as Backtrack, Kali, or a Wi-Fi Pineapple can
be used to perform a Man-in-the-Middle attack. An attacker can set
up a fake virtual or physical access point with the same SSID name as
the legitimate coffee shop access point. Unknowing users may connect
to this seemingly innocent access point and proceed to remotely con-
nect to their corporate network over the VPN. The Fake Access Point
(AP) can be used to terminate the encryption tunnel, and create a sec-
ondary VPN tunnel to the corporate network. By terminating the
encryption tunnel at the Fake AP allows the attacker to decrypt the
traffic and read it clear-text. In fact, this could also expose the corpo-
rate network and allow the attacker to perform further attacks on the
corporate environment (Figure 2.3).
Note that these same attacks could be performed on an enterprise
guest Wi-Fi network as well! A corporate guest Wi-Fi network is
designed for contractors and guests, but is also commonly used by
8 http://hakshop.myshopify.com/products/wifi-pineapple