Page 135 - Modelling in Transport Phenomena A Conceptual Approach
P. 135
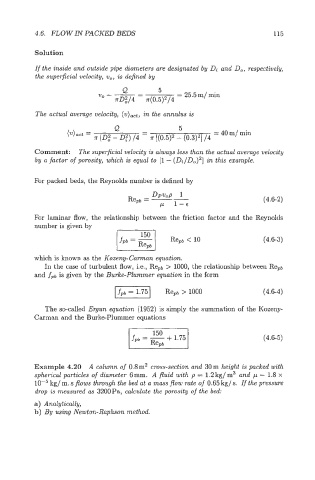
4.6. FLOW IN PACKED BEDS 115
Solution
If the inside and outside pipe diameters are designated by Di and Do, respectively,
the supeTficia1 velocity, vo, is defined by
Q 5
uo=-- = 25.5 m/ min
xDz/4 - ~(0.5)~/4
The actual average velocity, (v),,t, in the annulus is
-
Q - 5 = 40 m/ min
= x (02 - DZ) /4 x [(0.5)2 - (0.3)2] /4
Comment: The superficial velocity is always less than the actual average velocity
by a factor of porosity, which is equal to [l - (Di/Do)2] in this example.
For packed beds, the Reynolds number is defined by
(4.6-2)
For laminar flow, the relationship between the friction factor and the Reynolds
number is given by
(4.6-3)
which is known as the Kozeny-Carman equation.
In the case of turbulent flow, Le., Rep6 > 1000, the relationship between Repb
and fpb is given by the Burke-Plummer equation in the form
(4.6-4)
The so-called Ergun equation (1952) is simply the summation of the Kozeny-
Carman and the Burke-Plummer equations
(4.6-5)
Example 4.20 A column of 0.8m2 cross-section nd 30m height is p eked with
spherical particles of diameter 6mm. A fluid with p = 1.2 kg/ m3 and p = 1.8 x
kg/ m. s flows through the bed at a mass flow rate of 0.65 kg/ s. If the pressure
drop is measured as 3200Pa, calculate the porosity of the bed:
a) Analytically,
b) By using Newton-Raphson method.