Page 505 - Modelling in Transport Phenomena A Conceptual Approach
P. 505
11.3. ABSORPTION WITH REACTION 485
11.3 GAS ABSORPTION INTO A LIQUID
DROPLET WITH REACTION
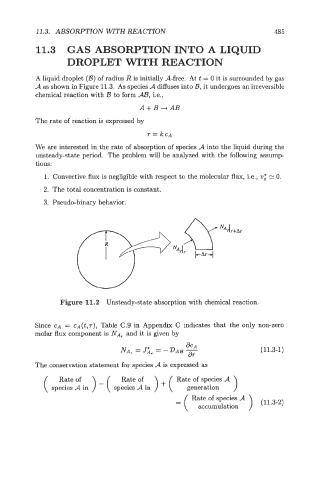
A liquid droplet (B) of radius R is initially A-free. At t = 0 it is surrounded by gas
A as shown in Figure 11.3. As species A diffuses into B, it undergoes an irreversible
chemical reaction with B to form AB, i.e.,
A+B-+AB
The rate of reaction is expressed by
r = kcA
We are interested in the rate of absorption of species A into the liquid during the
unsteady-state period. The problem will be analyzed with the following assump
tions:
1. Convective flux is negligible with respect to the molecular flu, Le., vz N 0.
2. The total concentration is constant.
3. PseudGbinary behavior.
Figure 11.2 Unsteady-state absorption with chemical reaction.
Since CA = cA(t,r), Table C.9 in Appendix C indicates that the only non-zero
molar flux component is NA, and it is given by
NA, = Jiv = -VAB - (11.3-1)
8CA
dT
The conservation statement for species A is expressed as
( species A in ) - ( species A in ) -t ( Rate of species A
Rate of
Rate of
generation
Rate of species A
accumulation