Page 218 -
P. 218
7 The Architecture 211
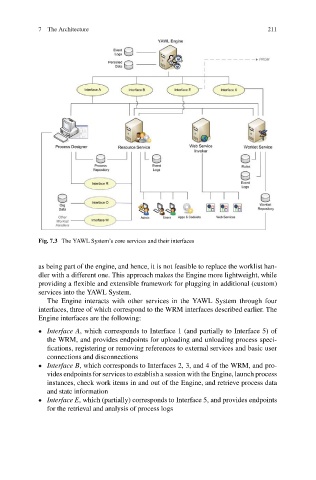
Fig. 7.3 The YAWL System’s core services and their interfaces
as being part of the engine, and hence, it is not feasible to replace the worklist han-
dler with a different one. This approach makes the Engine more lightweight, while
providing a flexible and extensible framework for plugging in additional (custom)
services into the YAWL System.
The Engine interacts with other services in the YAWL System through four
interfaces, three of which correspond to the WRM interfaces described earlier. The
Engine interfaces are the following:
Interface A, which corresponds to Interface 1 (and partially to Interface 5) of
the WRM, and provides endpoints for uploading and unloading process speci-
fications, registering or removing references to external services and basic user
connections and disconnections
Interface B, which corresponds to Interfaces 2, 3, and 4 of the WRM, and pro-
vides endpoints for services to establish a session with the Engine, launch process
instances, check work items in and out of the Engine, and retrieve process data
and state information
Interface E, which (partially) corresponds to Interface 5, and provides endpoints
for the retrieval and analysis of process logs