Page 39 -
P. 39
26 N. Russell and A. ter Hofstede
Branching Patterns
Branching patterns identify various types of branching behaviors that are generally
associated with split operators in a process. Four distinct types of split are commonly
delineated:
The AND-split, which diverges the thread of control in a given branch into
multiple concurrent execution threads in several branches.
The XOR-split (or the eXclusive OR-split), which routes the thread of control in
a given branch into one of several possible outgoing branches on the basis of an
execution decision made at runtime.
The OR-split, which routes the thread of control in a given branch into one,
several or all outgoing branches on the basis of an execution decision(s) made at
runtime.
The Thread-split, which diverges the thread of control in a given branch into
multiple concurrent execution threads in the same branch.
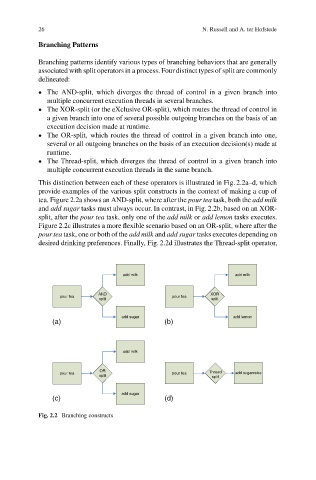
This distinction between each of these operators is illustrated in Fig. 2.2a–d, which
provide examples of the various split constructs in the context of making a cup of
tea. Figure 2.2a shows an AND-split, where after the pour tea task, both the add milk
and add sugar tasks must always occur. In contrast, in Fig. 2.2b, based on an XOR-
split, after the pour tea task, only one of the add milk or add lemon tasks executes.
Figure 2.2c illustrates a more flexible scenario based on an OR-split, where after the
pour tea task, one or both of the add milk and add sugar tasks executes depending on
desired drinking preferences. Finally, Fig. 2.2d illustrates the Thread-split operator,
add milk add milk
AND XOR
pour tea pour tea
split split
add sugar add lemon
(a) (b)
add milk
OR
pour tea pour tea Thread add sugarcube
split split
add sugar
(c) (d)
Fig. 2.2 Branching constructs