Page 47 -
P. 47
34 N. Russell and A. ter Hofstede
multiple instance task
A 1
merge split choice
split A 2 full join
A
A n
(a) (b)
multiple instance task
A 1 multiple instance task
A 1
split full join
split A 2 partial join
A n
A n+1 A n
(c) (d)
additional
instance
multiple instance task
A 1
multiple instance task
A 1 split join
split A 2 partial join disable A n
instance
creation
instance
additional creation A n+1
A n instance allowed
(e) (f)
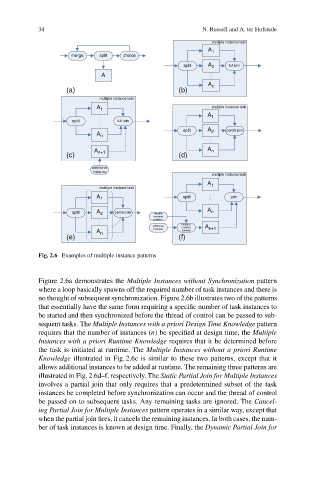
Fig. 2.6 Examples of multiple instance patterns
Figure 2.6a demonstrates the Multiple Instances without Synchronization pattern
where a loop basically spawns off the required number of task instances and there is
no thought of subsequent synchronization. Figure 2.6b illustrates two of the patterns
that essentially have the same form requiring a specific number of task instances to
be started and then synchronized before the thread of control can be passed to sub-
sequent tasks. The Multiple Instances with a priori Design Time Knowledge pattern
requires that the number of instances (n) be specified at design time, the Multiple
Instances with a priori Runtime Knowledge requires that it be determined before
the task is initiated at runtime. The Multiple Instances without a priori Runtime
Knowledge illustrated in Fig. 2.6c is similar to these two patterns, except that it
allows additional instances to be added at runtime. The remaining three patterns are
illustrated in Fig. 2.6d–f, respectively. The Static Partial Join for Multiple Instances
involves a partial join that only requires that a predetermined subset of the task
instances be completed before synchronization can occur and the thread of control
be passed on to subsequent tasks. Any remaining tasks are ignored. The Cancel-
ing Partial Join for Multiple Instances pattern operates in a similar way, except that
when the partial join fires, it cancels the remaining instances. In both cases, the num-
ber of task instances is known at design time. Finally, the Dynamic Partial Join for