Page 79 -
P. 79
66 N. Russell and A. ter Hofstede
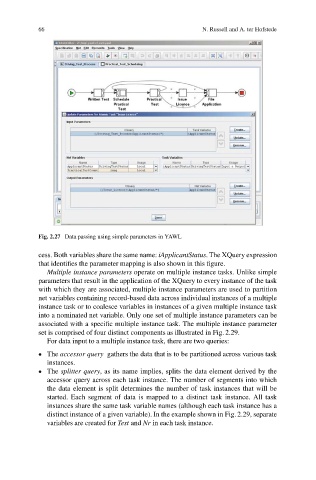
Fig. 2.27 Data passing using simple parameters in YAWL
cess. Both variables share the same name: iApplicantStatus. The XQuery expression
that identifies the parameter mapping is also shown in this figure.
Multiple instance parameters operate on multiple instance tasks. Unlike simple
parameters that result in the application of the XQuery to every instance of the task
with which they are associated, multiple instance parameters are used to partition
net variables containing record-based data across individual instances of a multiple
instance task or to coalesce variables in instances of a given multiple instance task
into a nominated net variable. Only one set of multiple instance parameters can be
associated with a specific multiple instance task. The multiple instance parameter
set is comprised of four distinct components as illustrated in Fig. 2.29.
For data input to a multiple instance task, there are two queries:
The accessor query gathers the data that is to be partitioned across various task
instances.
The splitter query, as its name implies, splits the data element derived by the
accessor query across each task instance. The number of segments into which
the data element is split determines the number of task instances that will be
started. Each segment of data is mapped to a distinct task instance. All task
instances share the same task variable names (although each task instance has a
distinct instance of a given variable). In the example shown in Fig. 2.29, separate
variables are created for Test and Nr in each task instance.