Page 99 -
P. 99
86 N. Russell and A. ter Hofstede
{user, role, var}
ExecutionType DistrEntityType
System Task Atomic Task
(name) (name)
is of .../...
{user, system, routing}
{random, round-robin-time,
AllocDirective
Software (name) round-robin-freq, round-robin-exp, is of .../...
Component shortest-queue}
to be performed by …/... (URI)
is governed by .../...
OrgExpr
(XQuery) DistrEntity
.../... is governed by ... can be distributed to .../... (id)
CapExpr
requires same user as .../...
(XQuery)
.../... is governed by ...
HistExpr User Task
(XQuery)
.../... is governed by ...
User Role Resource
.../offer initiated by ... .../allocation initiated by ... .../execution initiated by ... requires different user to…/... .../... has default privileges ... .../... has privileges ... .../is of...
TaskPrivs UserPriv ResourceType
(name)
(name) (name)
ActorType {user, role}
(name) {suspend, reallocate, {choose, concurrent, reorder,
reallocate_state, deallocate, viewteam, viewgroup,
{system, resource} piledexec, delegate, skip} chainexec, managecase}
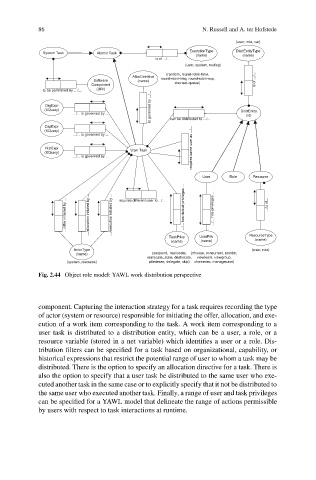
Fig. 2.44 Object role model: YAWL work distribution perspective
component. Capturing the interaction strategy for a task requires recording the type
of actor (system or resource) responsible for initiating the offer, allocation, and exe-
cution of a work item corresponding to the task. A work item corresponding to a
user task is distributed to a distribution entity, which can be a user, a role, or a
resource variable (stored in a net variable) which identifies a user or a role. Dis-
tribution filters can be specified for a task based on organizational, capability, or
historical expressions that restrict the potential range of user to whom a task may be
distributed. There is the option to specify an allocation directive for a task. There is
also the option to specify that a user task be distributed to the same user who exe-
cuted another task in the same case or to explicitly specify that it not be distributed to
the same user who executed another task. Finally, a range of user and task privileges
can be specified for a YAWL model that delineate the range of actions permissible
by users with respect to task interactions at runtime.