Page 58 - Modern Derivatization Methods for Separation Sciences
P. 58
Document Página 1 de 2
Page 19
detection (254 nm) is less sensitive than fluorescent derivatization and also the method requires the
evaporative elimination of excess PITC under reduced pressure after the reaction. The PITC derivatives
are fairly stable at room temperature, and the method has been used to determine the amino acid
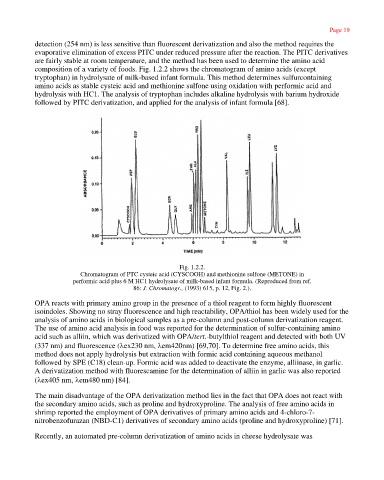
composition of a variety of foods. Fig. 1.2.2 shows the chromatogram of amino acids (except
tryptophan) in hydrolysate of milk-based infant formula. This method determines sulfurcontaining
amino acids as stable cysteic acid and methionine sulfone using oxidation with performic acid and
hydrolysis with HC1. The analysis of tryptophan includes alkaline hydrolysis with barium hydroxide
followed by PITC derivatization, and applied for the analysis of infant formula [68].
Fig. 1.2.2.
Chromatogram of PTC cysteic acid (CYSCOOH) and methionine sulfone (METONE) in
performic acid plus 6 M HC1 hydrolysate of milk-based infant formula. (Reproduced from ref.
86: J. Chromatogr., (1993) 615, p. 12, Fig. 2.).
OPA reacts with primary amino group in the presence of a thiol reagent to form highly fluorescent
isoindoles. Showing no stray fluorescence and high reactability, OPA/thiol has been widely used for the
analysis of amino acids in biological samples as a pre-column and post-column derivatization reagent.
The use of amino acid analysis in food was reported for the determination of sulfur-containing amino
acid such as alliin, which was derivatized with OPA/tert.-butylthiol reagent and detected with both UV
(337 nm) and fluorescence (λex230 nm, λem420nm) [69,70]. To determine free amino acids, this
method does not apply hydrolysis but extraction with formic acid containing aqueous methanol
followed by SPE (C18) clean-up. Formic acid was added to deactivate the enzyme, alliinase, in garlic.
A derivatization method with fluorescamine for the determination of alliin in garlic was also reported
(λex405 nm, λem480 nm) [84].
The main disadvantage of the OPA derivatization method lies in the fact that OPA does not react with
the secondary amino acids, such as proline and hydroxyproline. The analysis of free amino acids in
shrimp reported the employment of OPA derivatives of primary amino acids and 4-chloro-7-
nitrobenzofurazan (NBD-C1) derivatives of secondary amino acids (proline and hydroxyproline) [71].
Recently, an automated pre-column derivatization of amino acids in cheese hydrolysate was
http://emedia.netlibrary.com/nlreader/nlreader.dll?bookid=17968&filename=Page_19.html 30/09/2003